From Cotton to High-Tech Smart Textiles: Your Essential Guide to Choosing, Caring for, and Understanding Every Fabric Type
Fabrics shape our daily lives in ways we often don’t notice. From the sheets you sleep on to the clothes that protect you from weather, different types of fabric serve unique purposes. Over 100 different fabric types exist today, each with distinct properties that make them perfect for specific uses.
The world of textiles spans from natural materials like cotton and silk to modern synthetic innovations like polyester and nylon. Some fabrics excel at keeping us warm, while others help us stay cool. Canvas offers durability for outdoor use, while chiffon provides delicate beauty for formal wear.
Understanding what fabric is and how textiles work helps you make better choices for your clothing, home decor, and projects. This comprehensive guide will walk you through every major fabric type, their care requirements, and how to choose the right material for your needs.
Quick Answer: How Many Different Fabrics Are There?

Textile experts estimate there are over 1,000 different fabric types when you count all variations, blends, and specialty treatments. However, most fabrics fall into three main categories:
- Natural fabrics (from plants and animals)
- Synthetic fabrics (made from chemicals)
- Blended fabrics (combinations of natural and synthetic)
The most popular fabric types include cotton, polyester, wool, silk, linen, and denim. These six materials make up about 80% of all fabric production worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Natural and synthetic fabrics each offer unique benefits for different uses
- Proper fabric care extends garment life and maintains appearance
- Understanding fabric properties helps you choose the right material
- Sustainable fabric innovations are transforming the textile industry
- Care symbols and labels provide essential maintenance guidance
Natural Fibers: The Foundation of Textiles
Natural fibers create fabrics that excel in comfort and performance. Plants and animals provide these renewable materials that offer excellent breathability, durability, and moisture control. These traditional fabrics have been used for thousands of years and remain popular today.
Cotton Fabric: The Most Popular Natural Fiber
Cotton ranks as the most widely used natural fiber for clothing and home textiles. Its soft texture and excellent moisture absorption make it ideal for everyday wear. This versatile material gets softer with each wash and allows air to flow freely through the fabric.
Cotton Properties:
- Breathable and moisture-wicking
- Gets softer over time
- Available in different weights
- Easy to dye and print
- Naturally hypoallergenic
The material comes in different weights and weaves. Light cotton works well for summer shirts and dresses, while heavier cotton suits jeans and winter clothing. Cotton needs proper care to maintain its shape since it can shrink in hot water and may wrinkle easily.
Cotton Care Tips:
- Wash in cool water to prevent shrinkage
- Use gentle detergent for colors
- Air dry when possible to prevent damage
- Iron while slightly damp for best results
Linen Fabric: The Ancient Cooling Champion
Linen comes from the flax plant’s stem fibers and stands out for its exceptional cooling properties. The fabric’s loose structure creates tiny gaps that enhance airflow, making it perfect for hot weather clothing.
This durable fabric resists dirt and stains naturally. It grows stronger when wet and becomes softer over time with proper care. Linen works best for summer clothing, tablecloths, and bedding because of its natural texture and cooling effect.
While linen wrinkles easily, many people consider these creases part of its charm. The fabric lasts for years and often becomes an heirloom-quality material when cared for properly.
What makes linen special:
- Exceptional breathability for hot weather
- Gets stronger when wet
- Natural stain resistance
- Becomes softer with age
- Long-lasting durability
Silk Fabric: The Luxurious Protein Fiber
Silk offers unmatched smoothness and a natural sheen that catches light beautifully. This protein fiber comes from silkworm cocoons and creates lightweight yet strong fabric. Silk adjusts to body temperature, keeping you cool in summer and warm in winter.
The smooth fibers make silk gentle on skin and hair, which is why many people choose silk pillowcases and sleepwear. High-quality silk resists odors and dirt naturally while draping beautifully for elegant clothing.
Pure silk needs gentle care to maintain its quality. Hand washing in cool water helps preserve its natural properties and lustrous appearance.
Types of silk include:
- Mulberry silk (highest quality)
- Tussah silk (wild silk with texture)
- Charmeuse (satin weave silk)
- Crepe de chine (lightweight and flowing)
Wool Fabric: Nature’s Insulation System
Wool includes many varieties like cashmere, alpaca, and sheep’s wool. Each type offers different levels of softness and warmth. The fiber’s natural crimp creates air pockets that trap warmth while still allowing moisture to escape.
Wool can absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling wet. This unique property makes it comfortable to wear in various weather conditions. Wool naturally resists wrinkles and bounces back to shape easily.
The material works well for winter clothing, blankets, and suits. Its natural fire resistance adds an extra safety benefit that synthetic materials can’t match.
Traditional wool varieties:
- Merino wool (finest and softest)
- Cashmere (ultra-soft luxury fiber)
- Alpaca (warm and hypoallergenic)
- Lambswool (soft wool from young sheep)
Synthetic Fabrics: Modern Innovation in Textiles
Synthetic fabrics are manufactured through chemical processes to create materials with specific properties. These natural vs synthetic fabrics each serve different purposes, with synthetics offering excellent durability and performance features.
Polyester Fabric: The Versatile Synthetic
Polyester stands as the most common synthetic fabric worldwide. Made from petroleum-based products, it provides exceptional durability and resistance to wrinkles. Understanding polyester manufacturing helps explain why this fabric performs so well in everyday use.
The fabric maintains its shape well and dries quickly after washing. It resists wear and tear while being cost-effective to produce. These qualities make it ideal for everyday clothing and sportswear.
Key polyester features:
- Cost-effective production
- Colorfast and fade-resistant
- Blends well with natural fibers
- Easy to care for and wash
- Excellent shape retention
For a deeper understanding of polyester’s properties and uses, check out the complete polyester fabric guide.
Nylon Fabric: The Strong Performer
Nylon revolutionized the textile industry with its incredible strength and versatility. This strong and durable material excels in activewear and outdoor gear because of its excellent elasticity and quick-drying properties.
The fabric resists damage from oils and many chemicals while offering superior stretch recovery. These properties make nylon perfect for athletic wear, hosiery, and outdoor equipment.
Nylon benefits:
- High tensile strength for durability
- Water-resistant properties
- Excellent stretch recovery
- Lightweight yet tough
- Quick-drying capabilities
Acrylic Fabric: The Wool Alternative
Acrylic fabric serves as a wool alternative with superior warmth retention. It resists moths, oils, and chemicals while maintaining its shape better than natural wool. The material feels soft against skin and provides good insulation for cold weather.
Acrylic works well for sweaters, hats, and winter accessories. It combines well with other fibers to create optimal performance characteristics for specific uses.
Important acrylic characteristics:
- Quick-drying capabilities
- Resistant to sunlight damage
- Maintains warmth when wet
- Easy to clean and maintain
- Affordable wool substitute
Many garments combine acrylic with other fibers to create better performance. This synthetic material proves especially useful in cold-weather clothing where warmth and easy care matter most.
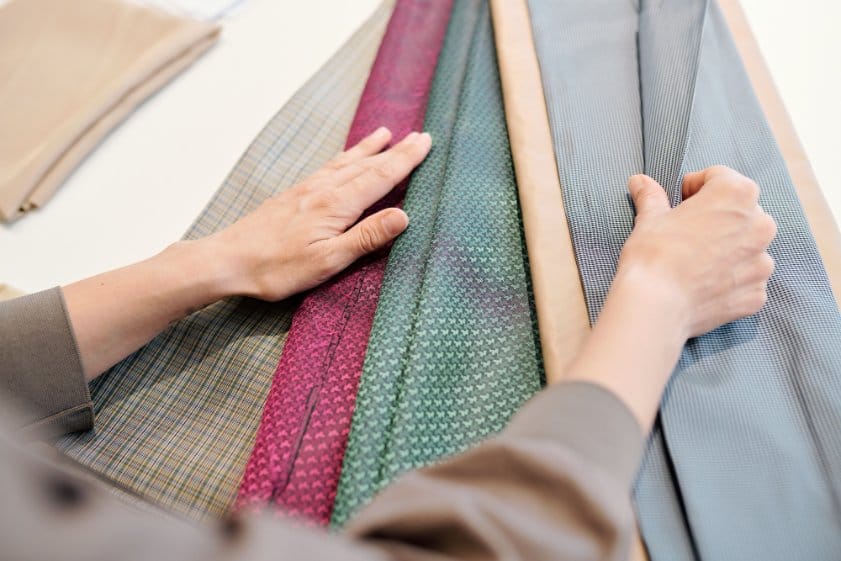
Woven Fabrics: Strength Through Structure
Woven fabrics are created by interlacing two sets of yarn at right angles. These fabrics are known for their strength, stability, and versatility in clothing and home textiles. The weaving process creates different patterns and textures that affect the fabric’s performance.
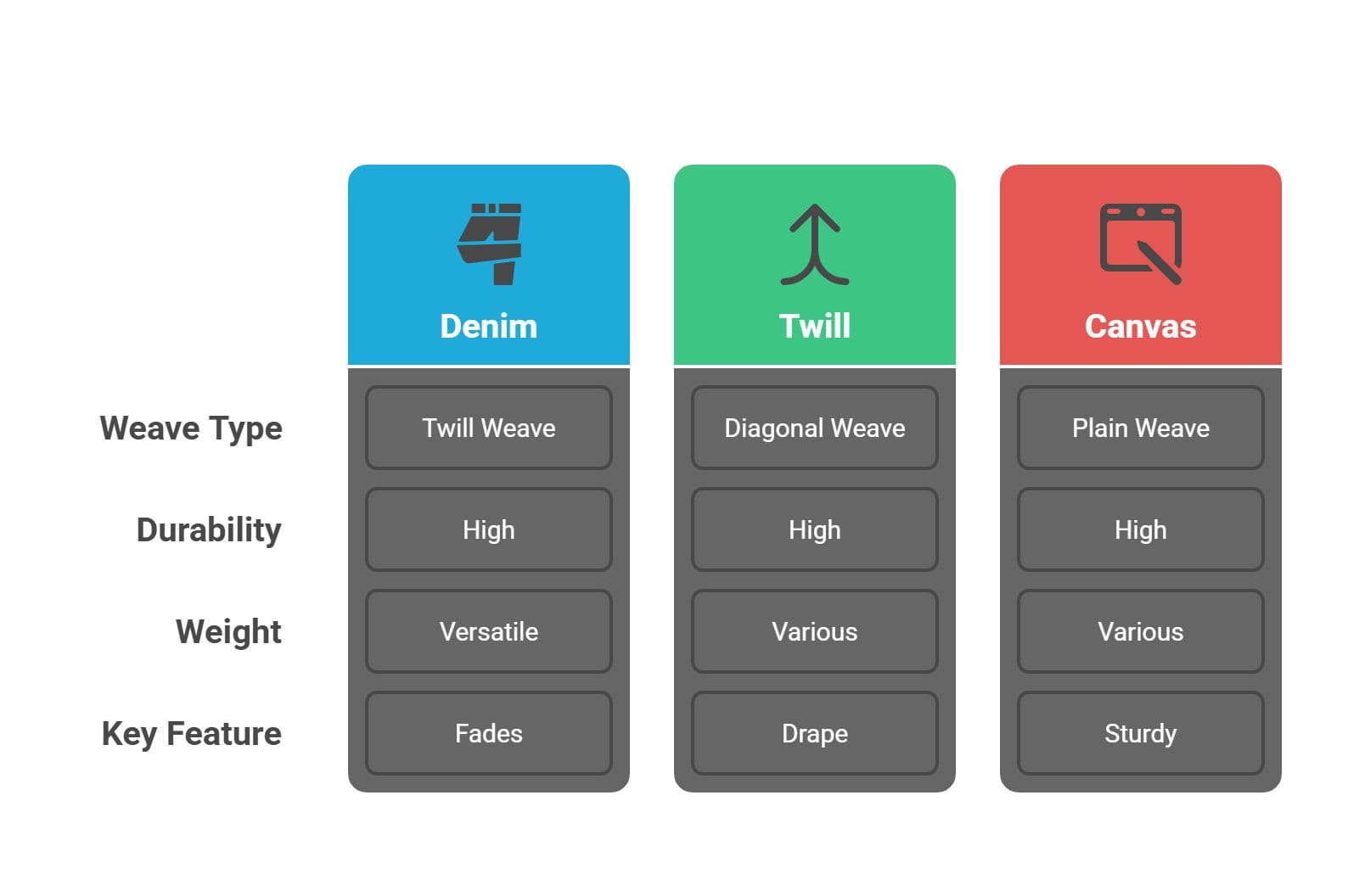
Denim: The Iconic Twill Weave
Denim fabric uses a twill weave with indigo-dyed cotton yarn. The blue warp threads pass over white weft threads to create its signature diagonal pattern. This construction gives denim its distinctive look and exceptional durability.
Classic denim has minimal stretch and excellent durability. The fabric becomes softer and develops unique wear patterns with use, which many people find appealing.
Common weights for denim range from 5 oz for lightweight shirts to 32 oz for heavy workwear. Most jeans use 12-16 oz denim, which provides the right balance of comfort and durability.
Key Denim Features:
- High tensile strength
- Fade-resistant construction
- Excellent breathability
- Gets better with age
- Versatile weight options
Twill Fabric: The Diagonal Pattern
Twill weave creates distinctive diagonal lines across the fabric surface. The pattern forms when weft threads pass over one or more warp threads, then under two or more warp threads in a repeated sequence.
Twill fabrics offer superior drape and wrinkle resistance compared to plain weaves. The diagonal structure helps hide stains and wear while providing excellent durability.
Common twill types:
- 2/1 twill (basic diagonal pattern)
- Herringbone twill (zigzag pattern)
- Diamond twill (diamond shapes)
- Gabardine (steep twill angle)
Canvas: The Heavy-Duty Plain Weave
Canvas is a plain-woven fabric made from heavy cotton or linen yarns. The tight weave structure creates a durable, sturdy material that handles heavy use well.
Traditional canvas uses unbleached cotton, but modern versions may include synthetic fibers for enhanced performance. This versatile fabric serves many purposes from bags to shoes.
Canvas applications:
- Bags and backpacks
- Shoes and boots
- Outdoor furniture
- Painting surfaces
- Heavy-duty clothing
Canvas comes in different weights measured in ounces per square yard. Lighter weights (8-12 oz) work well for clothing, while heavier weights (20+ oz) suit industrial applications.
Knitted Fabrics: Flexibility and Comfort

Knit fabrics are made by creating interlocking loops of yarn. These fabrics stretch easily and give excellent comfort due to their flexible structure. The knitting process creates different textures and stretch properties.
Jersey Knit: The T-Shirt Standard
Jersey knit is the most common type of knitted fabric. It features a smooth face side and a textured back side, making it perfect for comfortable everyday clothing.
Jersey knit has natural stretch in all directions, making it perfect for t-shirts and casual wear. Adding elastane can improve its recovery and shape retention for better fit.
Key jersey knit features:
- Lightweight and breathable
- Drapes well on the body
- Easy to care for
- Resists wrinkling
- Comfortable stretch
Rib Knit: The Stretchy Structure
Rib knit fabric creates raised vertical lines through alternating knit and purl stitches. This structure gives it excellent stretch, especially from side to side.
The ribbed texture makes this fabric ideal for necklines, cuffs, form-fitting garments, and athletic wear. Rib knit offers superior elasticity and recovers its shape well after stretching.
Rib knit uses:
- Necklines and cuffs
- Form-fitting garments
- Athletic wear
- Winter accessories
- Stretch panels
The textured surface provides extra warmth and insulation compared to regular jersey knit, making it popular for cooler weather clothing.
Decorative Fabrics: Beauty and Luxury

Decorative fabrics add visual interest and luxury to interior spaces through intricate patterns, rich textures, and elegant designs. These specialty textiles create depth and sophistication in home decor and formal wear.
Lace: The Delicate Web
Lace fabric creates delicate web-like patterns through skilled craftsmanship. It can be made from cotton, silk, linen, or synthetic materials like polyester and rayon.
The open, airy patterns range from floral designs to geometric shapes. Machine-made lace offers affordability, while handmade varieties provide unique artisanal quality.
Common uses include curtains, table linens, and decorative overlays. The transparent nature of lace creates soft light filtering effects when used for window treatments.
Lace varieties:
- Chantilly lace (floral patterns)
- Venetian lace (raised designs)
- Guipure lace (heavy patterns)
- Bobbin lace (handmade technique)
Velvet: The Luxurious Pile
Velvet features a dense pile of short fibers that create its signature soft, plush surface. The fabric reflects light differently when brushed in various directions, producing a dimensional appearance.
Modern velvets come in cotton, silk, or synthetic blends. Each type offers different levels of durability and sheen. Silk velvet provides the most luxurious feel, while cotton velvet offers better durability.
The rich texture makes velvet ideal for upholstery, throw pillows, and dramatic window treatments. It adds warmth and luxury to formal spaces.
Brocade: The Raised Pattern Fabric
Decorative brocade features raised patterns woven directly into the fabric. The designs often include florals, damasks, and paisley motifs that create visual depth and texture.
Traditional silk brocades represent the height of luxury textile craftsmanship. Modern versions incorporate metallic threads and synthetic fibers for added shimmer and durability.
This sturdy fabric works well for upholstery, wall coverings, and formal drapery. The textured surface hides wear in high-traffic areas while maintaining its elegant appearance.
Specialty Fabrics: Purpose-Built Materials

Specialty fabrics serve unique purposes in both industrial and commercial applications. These materials offer specific properties that make them ideal for specialized uses, from clothing to upholstery.
Leather: The Durable Hide
Leather is a durable material made from treated animal hides. The tanning process transforms raw skin into a flexible, long-lasting fabric that improves with age.
Natural leather comes in several grades. Full-grain leather is the highest quality, showing natural markings and developing a beautiful patina over time. Top-grain leather offers good durability with a more uniform appearance.
Faux leather provides an animal-free alternative using PVC or polyurethane bases to mimic genuine leather’s look and feel. Many faux options offer good water resistance and easy maintenance.
Leather types:
- Full-grain (highest quality)
- Top-grain (uniform appearance)
- Split leather (lower cost)
- Patent leather (glossy finish)
Suede: The Soft Napped Surface
Suede comes from the underside of animal skin, creating a soft, napped surface. This specialty fabric adds luxury to shoes, jackets, and accessories with its distinctive texture.
The short fibers of suede create a unique appearance that feels soft to touch. Regular brushing helps maintain its characteristic nap and prevents matting.
Synthetic suede, also called microsuede, offers similar properties to natural suede. These materials resist water better than natural suede and require less maintenance.
Vinyl: The Weather-Resistant Coating
Vinyl fabric consists of a synthetic material with a plastic coating. Its water-resistant properties make it perfect for outdoor furniture and marine applications.
Marine-grade vinyl includes UV inhibitors to prevent sun damage. This type stands up well to harsh weather conditions and salt water exposure without cracking or fading.
Contract-grade vinyl serves commercial spaces like restaurants and hospitals. These materials meet strict durability standards and offer antimicrobial properties for health and safety.
Vinyl comes in various thicknesses and textures. Heavy-duty options work well for upholstery, while lighter weights suit clothing and accessories.
Performance Fabrics: Technology Meets Textiles
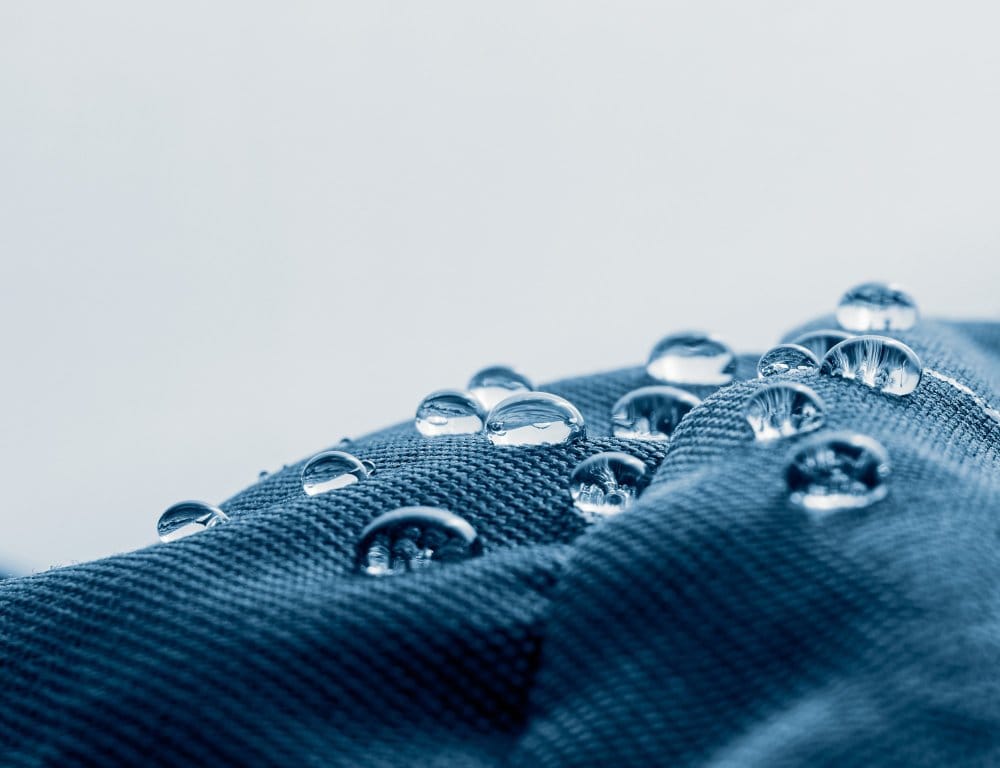

Performance fabrics use special materials and coatings to enhance clothing during physical activity. Advanced textile technology creates fabrics that keep athletes comfortable and dry while providing specific benefits like water resistance or fire resistance.
Moisture-Wicking Fabrics: Staying Dry
Polyester leads the pack in moisture management for athletic wear. The synthetic fibers pull sweat away from skin and spread it across the fabric surface for quick evaporation.
High-tech performance materials like nylon and spandex blends add stretch while maintaining moisture-wicking abilities. This combination works great for running and high-intensity workouts.
Many moisture-wicking fabrics now include antimicrobial treatments to prevent odor buildup. The treated fibers stop bacteria growth that causes unpleasant smells during exercise.
Moisture-wicking benefits:
- Quick sweat removal from skin
- Fast fabric drying
- Odor-resistant treatments
- Comfortable during exercise
- Maintains body temperature
Thermal Fabrics: Temperature Regulation
Merino wool stands out as a natural thermal fabric that regulates body temperature. The fine wool fibers trap warm air while still allowing excess heat to escape.
Advanced synthetic fleece provides excellent insulation without bulk. These lightweight materials create warm layers perfect for cold-weather activities and outdoor sports.
Modern thermal fabrics often combine different fiber types. A wool-polyester blend delivers both warmth and moisture control, making it ideal for winter sports and outdoor activities.
Water-Resistant and Waterproof Technologies
Understanding the difference between water-resistant vs waterproof fabrics helps you choose the right protection level. Water-resistant fabrics repel light moisture, while waterproof materials provide complete protection.
DWR coating (Durable Water Repellent) treatments make regular fabrics shed water. This water repellent technology creates a protective layer that causes water to bead up and roll off.
Many outdoor clothing brands use water-resistant fabric treatments to provide protection from light rain and snow. These treatments work well for everyday weather protection.
Eco-Friendly Fabrics: Sustainable Textile Innovation

Sustainable textile options reduce environmental impact while providing excellent durability and comfort. Natural plant-based materials require fewer chemicals and water during production, making them better choices for the environment.
Bamboo Fabric: The Fast-Growing Alternative
Bamboo creates versatile and sustainable textiles that feel soft against the skin. The fast-growing plant needs minimal water and no pesticides to thrive, making it an excellent eco-friendly choice.
Raw bamboo fibers undergo processing to create fabric with natural antibacterial properties and excellent moisture-wicking abilities. The resulting material feels silky and drapes well.
Key bamboo benefits:
- Naturally hypoallergenic
- Breathable in hot weather
- Biodegradable at end of life
- Requires less land than cotton
- Antibacterial properties
Hemp Fabric: The Soil-Improving Fiber
Hemp stands out as one of the most eco-friendly natural fibers available. The hardy plant improves soil health by removing toxins and heavy metals while growing.
Hemp fabric offers exceptional strength and durability that increases with washing. The material becomes softer with each wash while maintaining its shape and structure.
Hemp textile benefits:
- Uses 50% less water than cotton
- Grows without pesticides
- Absorbs carbon dioxide during growth
- Lasts many years with proper care
- Natural UV resistance
The natural UV resistance makes hemp ideal for outdoor clothing and upholstery. Its antimicrobial properties help prevent odors and bacterial growth.
Innovative Sustainable Materials
The textile industry continues developing new sustainable materials from unexpected sources:
Bio-based innovations:
- Mushroom leather from mycelium
- Seaweed-based fibers
- Pineapple leaf textiles
- Orange peel fabrics
- Algae-derived materials
These materials represent the future of sustainable fashion, offering alternatives to resource-intensive traditional fabrics while maintaining performance and style.
Fabric Blends: Best of Both Worlds

Fabric blends combine different fibers to create materials with enhanced properties. These combinations produce textiles that maximize strengths while minimizing weaknesses of individual fiber types.
Blended Cotton: Enhanced Performance
Cotton-polyester blends are among the most common mixed fabrics. The typical ratio is 65% polyester and 35% cotton, though other combinations exist for specific purposes.
These blends merge cotton’s natural softness and breathability with polyester’s strength and wrinkle resistance. The result is a fabric that maintains comfort while offering better durability.
The addition of polyester makes these blends more durable and easier to care for. They dry quickly and maintain their shape after washing, making them practical for everyday use.
Wool Blends: Comfort and Performance
Wool combines well with other fibers like cashmere, cotton, and synthetic materials. These blends offer improved properties while maintaining wool’s natural benefits.
Cotton-wool blends offer warmth while staying comfortable against the skin. These blends reduce wool’s tendency to feel scratchy or irritating for sensitive skin.
Adding synthetic fibers to wool creates more affordable options that still provide good insulation. These blends often resist wear better than pure wool while maintaining thermal properties.
Popular wool blends:
- Wool-cashmere (ultra-soft luxury)
- Wool-cotton (comfortable warmth)
- Wool-synthetic (affordable performance)
- Wool-silk (elegant drape)
The mixing of fibers helps control shrinkage, a common issue with pure wool garments. Blended fabrics often require less special care than pure natural fibers.
Fabric Care Guide: Maintaining Your Textiles
Proper fabric care extends garment life and maintains appearance. Understanding different fabric needs helps you keep your clothes and textiles looking their best for years to come.
Understanding Care Symbols
Care labels provide essential information about how to properly maintain your fabrics. These universal symbols tell you the safest methods for washing, drying, and ironing different materials.
| Symbol | Meaning | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| 🛁 with number | Water temperature | Number shows max temperature (30°C, 40°C, etc.) |
| Hand in water | Hand wash only | Use cool water and gentle detergent |
| Circle | Dry cleaning | Professional cleaning required |
| Square with circle | Tumble dry | Dots indicate heat level (1=low, 3=high) |
| Iron symbol | Ironing | Dots show temperature setting |
Fabric-Specific Care Instructions
Different fabrics require different care approaches to maintain their properties and appearance:
Cotton Care:
- Wash in cool water to prevent shrinkage
- Use gentle detergent for colored fabrics
- Air dry when possible to prevent damage
- Iron while slightly damp for best results
Silk Care:
- Hand wash in cool water with silk detergent
- Never wring or twist the fabric
- Roll in towel to remove excess water
- Air dry away from direct sunlight
- Iron on low heat with pressing cloth
Wool Care:
- Use wool-specific detergent
- Wash in cool water on gentle cycle
- Lay flat to dry to maintain shape
- Steam instead of ironing when possible
Synthetic Care:
- Machine wash in warm water
- Use regular detergent
- Tumble dry on low heat
- Remove promptly to prevent wrinkles
Stain Removal Guide
Quick action prevents stains from setting permanently. Different stain types require specific treatment methods:
Common stain treatments:
- Grease stains: Apply dish soap directly, let sit, then wash
- Blood stains: Rinse in cold water, treat with hydrogen peroxide
- Grass stains: Pre-treat with enzyme detergent
- Sweat stains: Use white vinegar or baking soda paste
- Wine stains: Blot immediately, treat with salt or club soda
Seasonal Fabric Care Tips
Different seasons require adjusted care routines to protect fabrics from weather-related damage:
Summer care:
- Wash frequently to remove sweat and sunscreen
- Use UV-protective detergents for outdoor gear
- Store winter fabrics in breathable garment bags
Winter care:
- Allow wet fabrics to dry completely before storing
- Use fabric softener to reduce static
- Protect from moth damage with cedar or lavender
Understanding Fabric Properties
Knowing fabric properties helps you choose the right material for your specific needs. Different fabrics excel in different areas based on their construction and fiber content.
Durability and Strength
Some fabrics last longer than others due to their fiber strength and construction. The most durable fabrics for everyday wear include denim, canvas, and wool blends.
Most durable fabrics:
- Denim (cotton twill weave)
- Canvas (heavy plain weave)
- Wool (natural elasticity)
- Nylon (synthetic strength)
- Polyester blends (shape retention)
Weight Classifications
Fabric weight affects drape, warmth, and durability. Understanding lightweight vs heavyweight fabrics helps you choose appropriately for your project.
| Weight Category | GSM Range | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Ultra-light | 50-100 GSM | Scarves, linings |
| Light | 100-200 GSM | Summer shirts, dresses |
| Medium | 200-350 GSM | Pants, jackets |
| Heavy | 350-500 GSM | Coats, upholstery |
| Extra Heavy | 500+ GSM | Outerwear, canvas |
Seasonal Fabric Selection
Choose fabrics based on climate and intended use. Breathable fabrics for summer include linen, cotton, and bamboo, while warm fabrics for winter clothing include wool, fleece, and down alternatives.
Summer fabric priorities:
- Moisture-wicking properties
- Breathability and airflow
- UV protection
- Quick-drying abilities
- Lightweight construction
Winter fabric priorities:
- Insulation and warmth
- Wind resistance
- Moisture management
- Layering compatibility
- Durability in harsh conditions
Specialized Fabric Categories

Soft and Comfortable Fabrics
For sensitive skin or maximum comfort, certain fabrics stand out. The softest fabrics for skin include bamboo, modal, and high-quality cotton.
What fabric is soft and fluffy? Fleece, chenille, and brushed cotton create the softest, fluffiest textures. These fabrics undergo special finishing processes that raise the surface fibers, creating a plush feel.
The softest most luxurious fabric: Cashmere tops the list for luxury and softness, followed by silk charmeuse and high-end cotton sateen. These materials offer unmatched comfort and elegant drape.
Stretch and Recovery Fabrics
Stretchy fabrics for comfort include spandex blends, jersey knits, and ribbed materials. These fabrics move with your body while maintaining their shape.
Stretch fabric types:
- Two-way stretch: Stretches in one direction (width or length)
- Four-way stretch: Stretches in both directions
- Recovery stretch: Returns to original shape after stretching
Thin and Sheer Fabrics
What do you call very thin fabric? Sheer fabrics include chiffon, georgette, organza, and tulle. These lightweight materials are nearly transparent and often used for layering or decorative purposes.
Characteristics of thin fabrics:
- Low GSM weight (under 100)
- Semi-transparent appearance
- Delicate handling required
- Often used for overlays
- Need special sewing techniques
Textured and Fuzzy Fabrics
What is fuzzy fabric called? Fuzzy fabrics include fleece, sherpa, faux fur, and brushed cotton. These materials have raised surface fibers that create a soft, fuzzy texture.
Types of textured fabrics:
- Fleece: Synthetic fuzzy fabric
- Sherpa: Wool-like textured fabric
- Corduroy: Ribbed texture fabric
- Bouclé: Looped yarn fabric
- Jacquard: Woven pattern fabric
Global and Traditional Fabrics

Traditional and Historic Fabrics
What are the three traditional fabrics? The three most traditional fabrics are cotton, wool, and silk. These have been used for thousands of years across different cultures and remain popular today.
What are the oldest types of fabric? Linen is considered the oldest fabric, with evidence of use dating back 34,000 years. Wool and cotton followed, with silk developing later in ancient China.
Regional Fabric Specialties
What is Nigerian fabric called? Nigerian textiles include Ankara (wax print), Aso-oke (hand-woven strips), and Adire (tie-dye). These fabrics feature bold patterns and vibrant colors representing Nigerian cultural heritage.
Other notable regional fabrics:
- Japanese: Silk kimono fabrics, cotton yukata
- Indian: Khadi cotton, silk sarees, block prints
- Scottish: Wool tartans, Harris tweed
- Peruvian: Alpaca wool, traditional weaves
Luxury and Rare Fabrics
What is the rarest fabric? Vicuña wool is considered the rarest and most expensive fabric. It comes from vicuñas, relatives of llamas, and can only be harvested every few years. Prices can exceed $3,000 per yard.
What are some fancy fabrics? Luxury fabrics include:
- Vicuña wool (rarest and most expensive)
- Sea silk (from clam fibers)
- Lotus silk (from lotus stems)
- Qiviut (musk ox fiber)
- Golden spider silk (extremely rare)
Silk-Like Alternatives
What fabric looks like silk but isn’t? Several fabrics mimic silk’s appearance:
- Rayon: Made from wood pulp, drapes like silk
- Polyester satin: Synthetic with silk-like sheen
- Modal: Soft texture similar to silk
- Acetate: Lustrous synthetic alternative
- Tencel: Sustainable silk-like fiber
What is the silky fabric called? Charmeuse, satin, and silk dupioni are specific types of silk fabrics. Charmeuse has a lustrous front and matte back, while satin refers to the weave structure that creates the smooth, shiny surface.
Industry Trends and Innovations
2025 Fabric Innovations
The textile industry continues evolving with new technologies and materials. Smart fabrics integrate electronics for health monitoring and temperature control. Self-healing textiles can repair small tears automatically.
Emerging technologies:
- Temperature-regulating fabrics
- Antibacterial treatments
- Self-cleaning properties
- Color-changing materials
- Embedded sensors
Sustainability Trends
Environmental concerns drive innovation in sustainable textiles. Bio-based materials from agricultural waste offer alternatives to traditional fibers. Closed-loop recycling systems reduce textile waste.
Sustainable developments:
- Mushroom-based leather alternatives
- Seaweed and algae fibers
- Recycled ocean plastic fabrics
- Waterless dyeing technologies
- Biodegradable synthetic alternatives
Digital Textile Revolution
Digital printing reduces water usage and allows for custom designs. 3D knitting creates seamless garments with zero waste. AI helps predict fashion trends and optimize fabric selection.
Plain and Common Fabric Names
What are the names of plain fabrics?
Plain fabrics refer to simple weave structures without complex patterns:
Plain weave fabrics:
- Muslin: Lightweight cotton plain weave
- Percale: Crisp cotton bedding fabric
- Poplin: Smooth cotton with slight ribbing
- Cambric: Fine cotton or linen plain weave
- Calico: Unbleached cotton plain weave
- Cheesecloth: Loose plain weave cotton
What is the most popular type of fabric? Cotton remains the most popular fabric globally, accounting for about 27% of all fiber production. Polyester follows closely at 25%, making these two the dominant materials in textile manufacturing.
Specialty Fabric Categories
What are Specialty fabrics? Specialty fabrics are engineered for specific purposes beyond basic clothing. These include:
- Technical textiles: Industrial and medical applications
- Smart fabrics: Electronic integration
- Performance fabrics: Engineered to resist creasing
Fabric Selection Guide
Selecting the appropriate fabric depends on several factors including intended use, care requirements, budget, and personal preferences. This decision tree helps guide your choice:
Choosing the Right Fabric for Your Project
Make informed decisions with our interactive fabric selection guide tailored to your specific needs and priorities.
Fabric Comparison Chart
| Fabric Type | Durability | Comfort | Care Level | Price Range | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Easy | Low-Medium | Everyday wear, bedding | ||
| Polyester | Very Easy | Low | Activewear, blends | ||
| Wool | Medium | High | Winter wear, suits | ||
| Silk | Difficult | Very High | Luxury, formal wear | ||
| Linen | Medium | Medium | Summer clothing, home decor | ||
| Bamboo | Easy | Medium | Eco-friendly clothing |
💡 Pro Tips for Fabric Selection
🎯 Consider Your Lifestyle
Choose low-maintenance fabrics if you have a busy schedule. Polyester blends and cotton are great for everyday wear.
🌡️ Think About Climate
Lightweight, breathable fabrics like linen and cotton work best in hot climates, while wool excels in cold weather.
💧 Check Care Requirements
Always read care labels before purchasing. Some fabrics require special cleaning that can add to long-term costs.
🔄 Test Before Committing
Buy a small sample first for large projects. This helps you check texture, drape, and care requirements.
Common Fabric Uses by Category
Understanding common fabric types and their uses helps you make informed decisions for different projects:
Clothing Applications:
- T-shirts: Cotton jersey, bamboo, modal
- Jeans: Cotton denim, stretch denim blends
- Formal wear: Silk, wool suiting, cotton poplin
- Athletic wear: Polyester, nylon, spandex blends
- Winter coats: Wool, down-filled nylon, fleece
- Summer dresses: Cotton voile, linen, rayon
Home Textile Applications:
- Bedding: Cotton percale, bamboo, linen
- Curtains: Cotton, linen, polyester blends
- Upholstery: Wool, cotton canvas, synthetic blends
- Towels: Cotton terry, bamboo terry
- Tablecloths: Linen, cotton, polyester
Advanced Fabric Technologies
Smart Textiles Revolution
Smart textiles represent the future of fabric technology, integrating electronics and advanced materials to create responsive clothing. These fabrics can monitor health, regulate temperature, and even charge electronic devices.
Current smart fabric applications:
- Heart rate monitoring shirts
- Temperature-regulating jackets
- LED-embedded clothing
- Posture-correcting garments
- Moisture-sensing athletic wear
Nano-Technology in Textiles
Nano-treatments add properties to traditional fabrics without changing their feel or appearance:
Nano-enhanced properties:
- Stain resistance: Repels liquids and dirt
- Antimicrobial protection: Prevents bacteria growth
- UV protection: Blocks harmful sun rays
- Wrinkle resistance: Maintains smooth appearance
- Moisture management: Enhanced wicking properties
Bio-Fabrication Advances
Scientists now grow fabrics in laboratories using biological processes:
Lab-grown materials:
- Biofabricated leather: Grown from mushroom mycelium
- Lab-grown silk: Produced by genetically modified bacteria
- Algae-based fibers: Sustainable and biodegradable
- Bacterial cellulose: Ultra-pure and strong
Global Fabric Market Insights
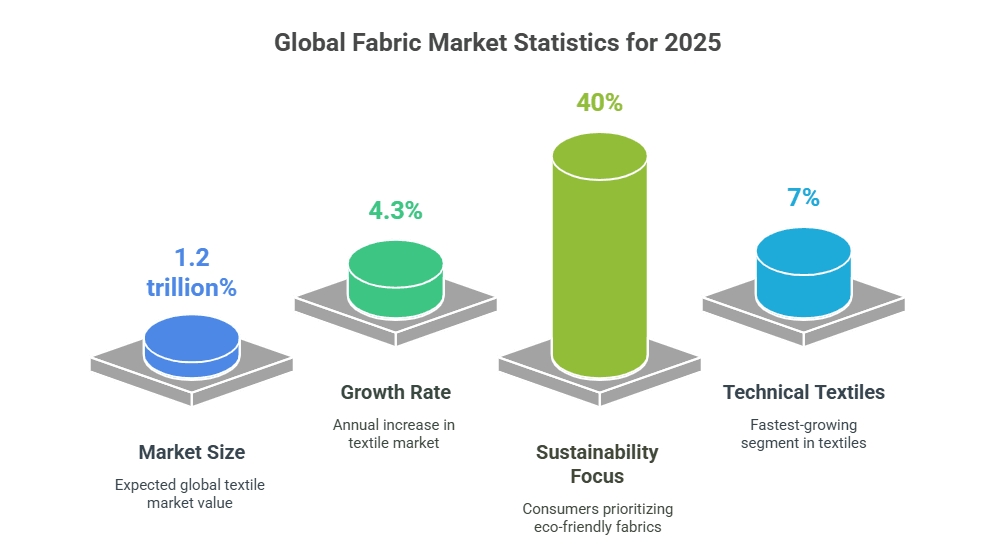
Market Trends and Statistics
The global textile market continues expanding, driven by population growth and rising living standards. Key statistics for 2025:
- Market size: Expected to reach $1.2 trillion globally
- Growth rate: 4.3% annual increase
- Leading producers: China, India, United States, Turkey
- Sustainability focus: 40% of consumers prioritize eco-friendly fabrics
- Technical textiles: Fastest-growing segment at 7% annually
Regional Fabric Preferences
Different regions show distinct fabric preferences based on climate, culture, and economic factors:
North America:
- Cotton dominates casual wear
- Performance fabrics for active lifestyles
- Growing interest in sustainable options
Europe:
- Strong demand for natural fibers
- Luxury fabric markets remain robust
- Leading in sustainable textile innovation
Asia-Pacific:
- Largest textile production region
- Rapid adoption of synthetic blends
- Traditional fabrics maintain cultural importance
Fabric Care Calculator and Tools
Smart tools to help you calculate care costs, compare options, and extend the life of your textiles.
Care Cost Calculator
Lifespan Estimator
Cost Comparison: Home Care vs Professional Cleaning
| Fabric Type | Home Wash Cost | Dry Clean Cost | Professional Care Frequency | Annual Cost Estimate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | $0.50 | $8.00 | As needed | $24-48 |
| Polyester | $0.50 | $8.00 | Rarely needed | $24-36 |
| Wool | $1.00 | $12.00 | 2-3 times per season | $36-72 |
| Silk | $2.00 | $15.00 | Always recommended | $90-180 |
| Cashmere | $3.00 | $20.00 | Professional only | $120-240 |
| Linen | $0.75 | $10.00 | Occasional | $36-60 |
Fabric Lifespan Guide
Expected lifespan with proper care (click items to see details):
💡 Money-Saving Care Tips
🏠 Master Home Care
Learn proper home washing techniques to reduce professional cleaning costs by up to 70%.
🕐 Time Your Cleaning
Many dry cleaners offer discounts on certain days. Tuesday-Thursday often have better rates.
🔄 Rotate Your Wardrobe
Let garments rest between wears. This can extend fabric life by 50% and reduce cleaning frequency.
🛡️ Preventive Care
Use garment bags, hangers, and proper storage to prevent damage and reduce cleaning needs.
Troubleshooting Common Fabric Problems
Fabric Damage Prevention
Preventing common fabric problems saves money and extends garment life:
Shrinkage Prevention:
- Always check care labels before washing
- Use cool water for natural fibers
- Air dry when possible
- Pre-shrink fabrics before sewing
Color Fade Prevention:
- Wash similar colors together
- Use color-safe detergents
- Avoid excessive sun exposure
- Turn garments inside out when washing
Pilling Reduction:
- Use fabric softener sparingly
- Wash inside out
- Avoid overloading washing machine
- Remove pills with fabric shaver
Emergency Fabric Care
Quick fixes for common fabric emergencies:
Immediate Stain Treatment:
- Act quickly – treat stains within 30 minutes
- Blot, don’t rub – prevents stain spreading
- Test treatments – check inconspicuous area first
- Work from outside in – prevents enlarging stain
- Rinse thoroughly – remove cleaning residue
Wrinkle Removal Without Iron:
- Hang in steamy bathroom
- Use wrinkle-release spray
- Roll in damp towel method
- Steam with kettle or steamer
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fabric Environmental Footprint
Understanding environmental impact helps make responsible choices:
Water Usage (per kilogram of fabric):
- Cotton: 2,700 liters
- Polyester: 70 liters
- Wool: 500 liters
- Linen: 400 liters
- Hemp: 300 liters
- Bamboo: 250 liters
Carbon Footprint Rankings (lowest to highest):
- Hemp (carbon negative)
- Linen (low impact)
- Organic cotton (reduced chemicals)
- Conventional cotton (moderate impact)
- Wool (methane concerns)
- Polyester (petroleum-based)
Sustainable Fabric Certification
Look for these certifications when choosing eco-friendly fabrics:
Major Certifications:
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): Organic fiber content
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100: No harmful chemicals
- Cradle to Cradle: Circular design principles
- BCI (Better Cotton Initiative): Sustainable cotton farming
- RDS (Responsible Down Standard): Ethical down sourcing
Future of Fabric Technology
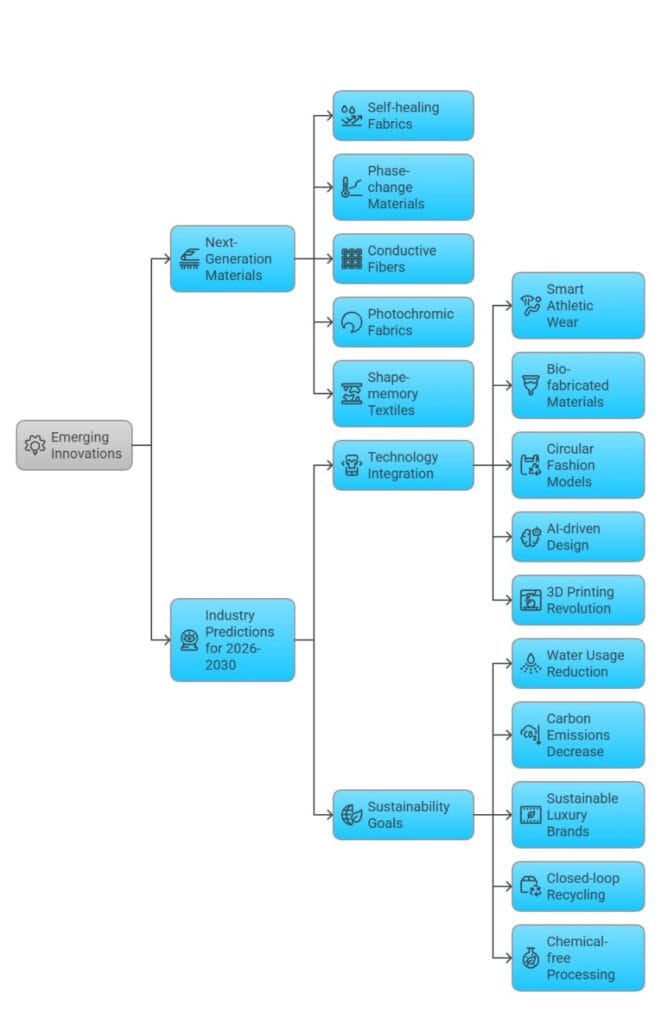
Emerging Innovations
The textile industry continues pushing boundaries with revolutionary innovations:
Next-Generation Materials:
- Self-healing fabrics: Repair minor tears automatically
- Phase-change materials: Adapt to temperature changes
- Conductive fibers: Enable electronic integration
- Photochromic fabrics: Change color with light exposure
- Shape-memory textiles: Return to predetermined forms
Industry Predictions for 2026-2030
Technology Integration:
- 25% of athletic wear will include smart features
- Bio-fabricated materials will reach commercial scale
- Circular fashion models will become standard
- AI-driven design will optimize fabric selection
- 3D printing will revolutionize textile production
Sustainability Goals:
- 50% reduction in textile water usage
- 30% decrease in carbon emissions
- 90% of luxury brands will use sustainable materials
- Closed-loop recycling systems will be widespread
- Chemical-free processing methods will expand
Conclusion
Understanding fabric types empowers you to make better decisions for your clothing, home décor, and creative projects. Each fabric serves specific purposes, from cotton’s everyday comfort to silk’s luxury appeal. The key lies in matching fabric properties to your intended use while considering care requirements and budget constraints.
The textile industry continues evolving with exciting innovations in sustainability and technology. Smart fabrics that monitor health, bio-based materials grown in laboratories, and recycled fibers from ocean waste represent the future of textiles. These advances address environmental concerns while maintaining the performance and comfort we expect from modern fabrics.
Key Recommendations
For Everyday Clothing: Choose cotton or cotton blends for comfort and breathability. Polyester blends offer durability and easy care for busy lifestyles. Consider bamboo fabrics for their softness and eco-friendly properties.
For Performance Activities: Select moisture-wicking synthetics like polyester or nylon for athletic wear. Look for four-way stretch fabrics that move with your body. Consider specialized treatments like antimicrobial finishes for extended wear.
For Luxury and Special Occasions: Invest in natural fibers like silk, wool, or high-quality cotton for special garments. These materials offer superior comfort and appearance but require more careful maintenance.
For Sustainability-Minded Consumers: Choose organic cotton, hemp, bamboo, or recycled materials when possible. Look for certifications like GOTS or OEKO-TEX that verify environmental and social standards. Consider the total lifecycle cost including care requirements.
For Home Textiles: Match fabric durability to usage levels. High-traffic upholstery needs strong fabrics like canvas or wool blends. Bedding benefits from breathable natural fibers like cotton or bamboo.
Final Thoughts
The world of fabrics offers endless possibilities for comfort, style, and functionality. By understanding different fabric types, their properties, and care requirements, you can make choices that serve your needs while supporting sustainable practices. Whether you’re selecting a cozy sweater, professional attire, or home décor, the right fabric choice enhances both performance and satisfaction.
As textile technology advances, new options will continue emerging. Stay informed about innovations in smart textiles, sustainable materials, and improved manufacturing processes. The future of fabrics promises even better performance, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced comfort for all our textile needs.
Remember that proper care extends fabric life significantly, making quality choices more economical over time. Invest in fabrics that match your lifestyle and maintenance preferences, and always follow care instructions to preserve their properties and appearance. With this knowledge, you’re equipped to navigate the diverse world of textiles confidently. textiles:** Athletic and outdoor use
- Protective fabrics: Fire-resistant, chemical-resistant
- Medical textiles: Surgical and therapeutic applications
Wrinkle Properties
What fabric is wrinkle-free? Polyester and polyester blends resist wrinkles naturally. Other wrinkle-resistant options include:
- Synthetic blends: Polyester-cotton combinations
- Treated fabrics: Wrinkle-free chemical treatments
- Jersey knits: Natural stretch prevents creasing
- Wool: Natural elasticity resists wrinkles
- Performance fabrics: Engineered to resist creasing
- Spandex blends: Elastane content maintains smooth appearance
- Modal: Semi-synthetic fiber with natural wrinkle resistance
- Bamboo: Naturally smooth fibers reduce creasing
Most wrinkle-prone fabrics:
- Linen: Wrinkles easily but many consider it part of its charm
- Cotton: Pure cotton creases readily without treatment
- Silk: Delicate fibers can wrinkle, especially lighter weights
- Rayon: Tends to wrinkle and may require careful handling
Wrinkle prevention tips:
- Choose blended fabrics over pure natural fibers
- Look for “wrinkle-free” or “easy-care” treatments
- Hang garments immediately after washing
- Use fabric softener to reduce static and stiffness
- Consider knit fabrics over woven for travel clothing
- Understanding wrinkle resistance helps you choose appropriate fabrics for your lifestyle, especially if you prefer low-maintenance clothing or travel frequently.
Frequently Asked Questions
General Fabric Questions
How can I tell if a fabric is natural or synthetic?
Natural fabrics usually feel softer and breathe better. Synthetic fabrics often have a slight sheen and may feel less breathable. Check the fabric label for fiber content – natural fabrics will list cotton, wool, silk, or linen, while synthetics show polyester, nylon, or acrylic.
Which fabrics are best for sensitive skin?
Bamboo, organic cotton, silk, and modal are excellent for sensitive skin. These fabrics are naturally hypoallergenic and have smooth fibers that don’t irritate. Avoid wool and synthetic blends if you have skin sensitivities.
Can I mix different fabric types in the same wash load?
It’s best to separate fabrics by care requirements. Natural fibers like cotton can usually be washed together, but keep delicate fabrics like silk separate. Always check care labels and group similar washing instructions.
Why do some fabrics pill and others don’t?
Pilling occurs when loose fibers tangle together on the fabric surface. Synthetic fabrics and low-quality natural fibers are more prone to pilling. Higher-quality fabrics with longer fibers pill less. Proper care, including gentle washing and using fabric softener sparingly, reduces pilling.
Care and Maintenance Questions
How often should I wash different types of clothing?
Underwear and socks should be washed after each wear. T-shirts and blouses can typically be worn 1-2 times before washing. Jeans can go 5-10 wears depending on activity level. Sweaters and jackets only need washing when visibly dirty or smelly.
What’s the difference between dry cleaning and regular washing?
Dry cleaning uses chemical solvents instead of water to clean fabrics. This method is gentler on delicate fabrics like silk and wool, and it prevents shrinkage and color bleeding. Regular washing uses water and detergent, which works well for most cotton and synthetic fabrics.
How can I prevent my clothes from shrinking?
Always read and follow care labels. Use cool water for washing, avoid high heat in the dryer, and consider air-drying delicate items. Pre-wash fabrics before sewing to account for any shrinkage. When in doubt, choose gentle cycle settings.
What should I do if colors bleed in the wash?
Stop the cycle immediately if you notice bleeding. Remove affected items and treat with cold water and white vinegar. For set-in color bleeding, try soaking in an oxygen bleach solution. To prevent bleeding, always wash new items separately the first few times and sort by color.
Buying and Selection Questions
How do I choose the right fabric weight for my project?
Consider the intended use and season. Lightweight fabrics (under 200 GSM) work well for summer clothing and linings. Medium weights (200-350 GSM) suit most clothing applications. Heavyweight fabrics (over 350 GSM) are ideal for coats, upholstery, and bags.
What makes one fabric more expensive than another?
Several factors affect fabric cost: fiber quality (natural fibers often cost more), manufacturing complexity (hand-woven vs. machine-made), brand reputation, certifications (organic, sustainable), and rarity (cashmere, silk). Processing methods and finishing treatments also influence price.
How can I tell if a fabric is good quality?
Check for even weave without loose threads, consistent color throughout, and appropriate weight for the fabric type. Quality fabrics feel smooth and substantial. Read fiber content labels – higher percentages of natural fibers or quality synthetics indicate better fabric. Established brands often provide better quality assurance.
Should I buy pre-shrunk fabrics?
Pre-shrunk fabrics save time and reduce risk of garment fit changes after washing. However, they may cost more. If buying regular fabrics, always pre-treat them according to your planned care method before cutting or sewing.




