Your Complete 2025 Guide to Cotton Fabric Types, Sustainability, Care & Uses
Cotton fabric is a soft, natural material used around the world for clothing, quilting, home decor, and many other purposes. People like cotton because it is comfortable, easy to care for, and gentle on the skin. Its breathable texture and simple cleaning make it a common choice for both new and experienced makers.
Cotton fabric comes in many types, weaves, and patterns. It can be found in plain, colorful, or patterned styles to match almost any project. This makes it one of the most versatile and practical fabrics available today.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Cotton fabric is valued for its comfort and use in many products
- It comes in different types, weaves, and colors
- Cotton works well for clothing, crafts, and decor
- Sustainable cotton options are becoming more important in 2025
- Proper care extends cotton’s lifespan and reduces environmental impact
What Is Cotton Fabric?
Cotton fabric is made from the fibers found in the seedpods of cotton plants. It is valued for being soft, breathable, and easy to use in many everyday items.
Understanding Cotton Basics
What is cotton fabric called? Cotton fabric goes by many names depending on its weave and finish. The most common terms include cotton cloth, cotton textile, or simply “cotton.” The technical term for cotton is “gossypium,” which is also the scientific name for the cotton plant family.
Is cotton natural or synthetic? Cotton is completely natural. Unlike synthetic fabrics like polyester, cotton comes directly from plant fibers. There is no synthetic cotton, though cotton can be blended with synthetic materials to create cotton blend fabrics.
Overview and Key Characteristics
Cotton fabric is known for its softness, making it gentle on the skin and comfortable to wear. People often choose cotton for clothing and sheets because it lets air flow, which helps keep the body cool. This makes cotton a good choice in warm weather.
Is cotton fabric good for summer? Yes, cotton is excellent for summer wear. Cotton is naturally breathable and absorbs moisture, helping to keep you cool and dry. The fibers allow air to move freely through the fabric, making it much more comfortable than synthetic alternatives in hot weather.
It is also popular for its breathable quality. The fibers can absorb moisture, helping to keep the wearer dry. Cotton fabric comes in different weights and textures, so it can be used for many types of garments, towels, and home decor items.
Working with cotton is simple because the fabric is strong and holds its shape well. It is also easy to dye, so it comes in many colors and patterns. Cotton’s wide use, from T-shirts to curtains, is due to these key features.
Origins and Production Process
Where does cotton come from? Cotton comes from the cotton plant, which grows in warm climates around the world. The largest cotton producers include the United States, China, India, and Brazil. The plant grows seedpods called bolls that fill with fluffy, white fibers as they mature.
How is cotton made? The process starts when farmers harvest the cotton bolls. After picking, the fibers are separated from the seeds in a process called ginning. The cleaned fibers are spun into yarn or thread. This yarn is then woven or knitted to make cotton fabric for clothing, bedding, and more.
Throughout history, cotton has been farmed in warm regions. Today, cotton is grown in many countries, supporting large textile industries. The process from field to fabric highlights how cotton is turned into a useful, soft, and versatile material.
Types Of Cotton Fabric
Cotton fabrics come in many forms, each with unique qualities suited for different uses. The properties of each type are shaped by factors like fiber length, weave, and finish.
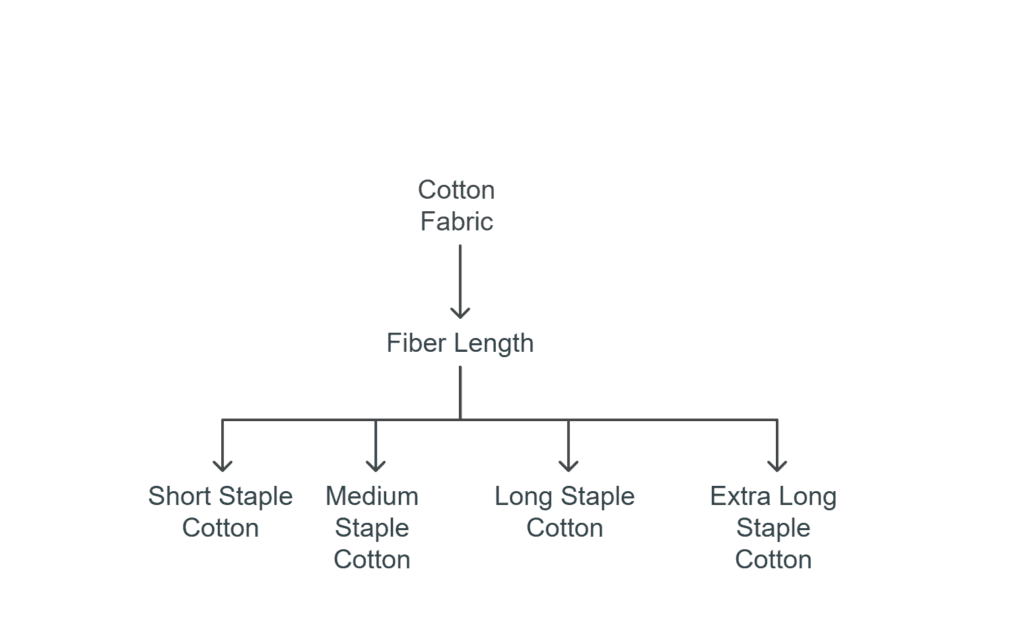
What Are The Four Main Types Of Cotton?
The four main classifications of cotton are based on fiber length and quality:
- Short Staple Cotton – Most common variety with fibers under 1 inch
- Medium Staple Cotton – Fibers between 1-1.25 inches, good for general use
- Long Staple Cotton – Premium fibers over 1.25 inches (like Pima cotton)
- Extra Long Staple Cotton – Luxury fibers over 1.4 inches (like Egyptian cotton)
100% Cotton Fabric
100% cotton fabric is made from pure cotton fibers. It is soft, breathable, and absorbent, making it a popular choice for clothes and bedding. Because it comes from natural fibers, it is often hypoallergenic and comfortable against the skin.
What is the most common cotton fabric? Plain weave cotton, often called “quilting cotton” or “cotton broadcloth,” is the most common type. This includes basic cotton used for everyday clothing like t-shirts and basic home textiles.
This type of fabric can be found in different weaves such as muslin, gauze, and poplin. Each weave affects the feel and strength of the fabric. For example, gauze is light and airy, muslin is soft and plain, while poplin is smooth and slightly crisp.
Does 100 cotton stretch? Pure 100% cotton has very little natural stretch. Cotton fibers themselves don’t stretch much, so the fabric moves mainly based on its weave. However, cotton can be blended with stretchy fibers like elastane to add flexibility.
In addition to being comfortable, 100% cotton is easy to care for and widely available. It can shrink in the wash if not pre-shrunk. Many people like it for its simple, classic feel and its ability to absorb dyes well, leading to bright, lasting colors.
Egyptian Cotton
Egyptian cotton is known for its long, fine fibers. Grown along the Nile River, these fibers can be spun into very soft and strong threads. This fabric is prized for its smooth texture and durability.
Because of the fiber length, Egyptian cotton sheets often feel softer and get even smoother over time. They also tend to be stronger and less likely to pill compared to standard cotton. These qualities make Egyptian cotton a premium choice for luxury bedding and bath towels.
Buyers should be aware that some products labeled as Egyptian cotton may not be pure. High-quality Egyptian cotton usually comes with certifications to prove its origin. People who prefer comfort and quality often choose this type, especially for items expected to last a long time.
Pima and Supima Cotton
Pima cotton is a high-quality, long-staple cotton grown primarily in the United States, Australia, and Peru. It produces softer, stronger, and more durable fabric than regular cotton.
Supima cotton is a premium version of Pima cotton that must meet strict quality standards and can only be grown in the United States. The name “Supima” stands for “Superior Pima” and represents the finest cotton fibers available.
Cotton Piqué
What is crisp cotton fabric called? One popular crisp cotton fabric is piqué (pronounced “pee-kay”). Cotton piqué is a knit fabric known for its raised, waffle-like or honeycomb texture. Originally developed in the 18th century, piqué found mainstream fame when tennis legend René Lacoste chose it for his revolutionary polo shirt in the 1920s.
Cotton piqué offers excellent breathability and a structured appearance that holds its shape well. In 2025, this fabric continues to be popular for polo shirts, casual wear, and premium garments that need both comfort and a polished look.
Flannel
Flannel is a soft, warm cotton fabric made using either 100% cotton or a blend with synthetic fibers. It is brushed on one or both sides to create a fuzzy, cozy texture. This results in better insulation, making flannel popular in colder climates.
Traditionally, flannel is used for shirts, pajamas, and bedding. It can come in plain colors or printed patterns, like the classic plaid. Cotton flannel tends to be both durable and comfortable, which explains its common use in items meant for warmth.
Flannel is easy to care for, though it may pill over time with heavy use. Its breathable nature keeps it from feeling too heavy while still providing warmth, making it a top choice for everyday wear and home textiles.
Not sure which cotton type is right for your project? Take our cotton type selector quiz to get personalized recommendations based on your specific needs and preferences.
Cotton Blends and Mixed Fabrics

What Is Cotton Blend Fabric?
What does cotton blend mean? A cotton blend is fabric made by combining cotton fibers with other materials, either natural or synthetic. Common blends include cotton-polyester, cotton-spandex, and cotton-modal combinations.
Difference Between Cotton And Cotton Blend
| Aspect | 100% Cotton | Cotton Blend |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability | Excellent | Good to excellent |
| Stretch | Minimal | Varies by blend |
| Durability | Good | Often better |
| Care | May shrink | Often easier care |
| Price | Varies | Often less expensive |
| Feel | Natural, soft | Depends on blend |
Cotton vs Polyester blends are popular because they combine cotton’s comfort with polyester’s durability and wrinkle resistance. A 60/40 cotton-polyester blend offers good breathability while being easier to care for than pure cotton.
Cotton blends can offer advantages like:
- Added stretch and recovery
- Better shape retention
- Reduced shrinkage
- Improved wrinkle resistance
- Lower cost
However, blends may sacrifice some of cotton’s natural benefits like breathability and moisture absorption.
Popular Cotton Weaves and Blends

Cotton fabric comes in many weave styles and blends, each offering unique textures, strengths, and uses. The type of weave affects how the fabric feels, drapes, and performs in daily life.
Cotton Canvas Fabric
Cotton canvas is known for its thick, sturdy weave. The fabric uses a plain weave pattern, which gives it high durability and strength. Many people use canvas for items that need to last, like tote bags, shoes, tents, and upholstery.
The surface of cotton canvas is usually rougher than other cotton fabrics. This makes it a good pick for projects that need extra wear and tear resistance. Heavier canvas fabrics are also used in workwear because they can take a lot of rough use. Cotton canvas can also be found in art, as many artists choose it as a painting surface because it holds paint well and is easy to stretch.
Some canvas fabrics are blended with polyester or nylon to make them even more tough and weather-resistant. Many canvas products can be washed at home, making them practical for busy lifestyles.
Poplin and Sateen
Poplin is a plain weave cotton fabric that feels smooth and crisp. Its yarns are fine, making it lightweight and breathable. Poplin is often used for shirts, dresses, and bed linens because it holds its shape well and feels soft against the skin. It resists wrinkles better than some other cotton weaves, which makes it a popular option for office wear.
Sateen is woven in a way that gives the fabric a soft, silky touch and a slight sheen. Unlike shiny polyester satins, sateen uses cotton fibers, so it is still breathable and easy to care for. The weave places more threads on the surface, creating a smooth finish. Sateen is common in bedsheets, pillowcases, and even some blouses.
What is shiny cotton fabric called? Sateen is the most common shiny cotton fabric, though other options include mercerized cotton and polished cotton, which get their shine through special treatments.
Both poplin and sateen may include small amounts of synthetic fibers for added stretch or wrinkle-resistance, though pure cotton varieties are widely available.
Muslin and Gauze
Muslin is a plain weave cotton fabric that is very lightweight and breathable. The texture is soft and slightly open, so air and moisture pass through easily. Muslin is used for baby blankets, reusable produce bags, dressmaking mockups, and even medical bandages.
What is a soft cotton fabric? Muslin is often considered one of the softest cotton fabrics, especially when it has been pre-washed. Other notably soft cotton fabrics include cotton jersey, flannel, and high-quality percale.
Muslin is available in various weights, from extra-fine to coarse. Heavier muslins are used for theater backdrops and lining clothing, while lighter versions are common in summer clothing and home textiles. Muslin wrinkles easily, but it can be ironed or steamed flat.
Gauze is even more loosely woven than muslin. This gives it a semi-transparent, airy feel. Double gauze is two layers of thin gauze fabric joined together, adding strength without losing breathability. Cotton gauze is often used in baby clothes, scarves, and swaddles because it’s gentle and soft.
Specialized Cotton Fabrics
What is the name of the crinkle cotton fabric? Seersucker is the most famous crinkle cotton fabric. It features alternating smooth and puckered stripes that create a naturally textured, wrinkle-resistant surface that’s perfect for summer clothing.
What is another name for cotton lawn fabric? Cotton lawn is sometimes called “lawn cotton” or simply “lawn.” It’s a fine, lightweight, plain-weave cotton fabric that’s smooth and crisp, often used for delicate clothing and handkerchiefs.
Cotton Fabric Sustainability and Environmental Impact

The Environmental Challenge
Cotton production has significant environmental impacts that consumers should understand. Traditional cotton farming uses about 2,700 liters of water to produce a single t-shirt and accounts for 25% of the world’s insecticide use.
Water Usage and Impact
Cotton Water Footprint by Type:
| Cotton Type | Water Usage (per kg) | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Cotton | 2,500-3,000 liters | High |
| Organic Cotton | 1,800-2,500 liters | Medium |
| Recycled Cotton | 500-800 liters | Low |
| Better Cotton (BCI) | 1,200-2,000 liters | Medium-Low |
The excessive water usage contributes to environmental stress, particularly in water-scarce regions. A stark example is the Aral Sea, which lost 90% of its volume due to cotton irrigation projects.
Sustainable Cotton Options
Organic Cotton: Grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, organic cotton is better for soil health and reduces chemical runoff. However, it often requires more land and water than conventional cotton.
Better Cotton Initiative (BCI): This program helps farmers use water more efficiently, care for soil health, and reduce harmful chemical use while improving livelihoods.
Recycled Cotton: Made from post-consumer or post-industrial cotton waste, recycled cotton uses 90% less water than conventional cotton and helps reduce textile waste.
Regenerative Cotton: Goes beyond organic by actively improving soil health, increasing biodiversity, and capturing carbon in the soil.
Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint of cotton varies by production method and usage:
- Growing and processing: 5-10 kg CO2 per kg of cotton
- Consumer use: 31-37% of total emissions come from washing and drying
- Transportation: Varies by distance and method
Sustainable Cotton Certifications
Look for these certifications when buying sustainable cotton:
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard)
- BCI (Better Cotton Initiative)
- OEKO-TEX Standard 100
- Cradle to Cradle Certified
- USDA Organic
Design, Color, and Texture
Cotton fabric offers many options for both style and comfort. It can be found in a variety of colors, surface designs, and tactile textures that appeal to many different tastes.
Solids, Patterns, and Prints
Cotton fabric comes in solid colors, which are popular for their clean and classic look. Solids can create a calm appearance and are often chosen for formal clothing, uniforms, and basics.
Patterns and prints add personality and variety. Common patterns include stripes, plaids, and polka dots. Printed cotton fabrics feature everything from floral designs to geometric shapes. These patterns are created through dyeing and printing techniques, which help colors stay bright even after washing.
Can you print on cotton fabric? Yes, cotton is excellent for printing. Its natural fibers absorb ink well, making it perfect for screen printing, digital printing, and heat transfer applications. Cotton’s smooth surface and good color retention make it a favorite for custom clothing and promotional items.
Quilters and crafters enjoy the range of options in cotton prints, as they mix and match for more interesting visual effects. When picking cotton fabric for a project, the choice between solids and prints depends on the desired mood, use, and style.
Softness and Feel
Cotton is known for its natural softness. The softness can change depending on the weave, finish, and treatment. For example, cotton flannel feels soft and cozy, while percale is smooth and crisp.
How do you soften cotton fabric? Several methods can make cotton softer:
- Wash with fabric softener or white vinegar
- Use tennis balls in the dryer
- Choose pre-washed cotton fabrics
- Avoid over-drying which can make fibers stiff
Texture matters for both comfort and appearance. Smooth, tightly woven cotton feels soft against the skin and looks polished, adding a sense of quiet elegance to shirts and dresses. Textured cotton, like seersucker or waffle weave, adds interest and may feel airy or slightly bumpy.
Touch is important because it affects how the fabric drapes and moves. Cotton’s breathability makes it a favorite for warm weather and active wear. Whether smooth or textured, cotton remains gentle and suitable for sensitive skin.
Performance and Qualities
Cotton fabric is valued for its strength, flexibility, and ability to allow air to pass through. These features make it useful for many types of clothing and household items.
Durability and Versatility
Cotton fibers have natural strength, which gives the fabric a good level of durability. Well-made cotton fabrics can handle regular washing and daily use without breaking down quickly. Many cotton items, such as shirts, sheets, and towels, keep their shape and quality for a long time when cared for properly.
Which is the best cotton fabric? The “best” cotton depends on your needs:
- For luxury bedding: Egyptian or Supima cotton
- For everyday wear: Pima or high-quality regular cotton
- For crafting: Quilting cotton with tight weave
- For summer clothes: Lightweight cotton lawn or poplin
- For durability: Cotton canvas or denim
This fiber is also very versatile. Cotton can be woven into fine, soft materials for dress shirts or thick, sturdy fabrics for jeans and workwear. Its ability to accept dyes and finishes easily means it is available in many colors and patterns.
Cotton also works well in blends. It is often mixed with synthetic fibers to create fabrics that combine the best qualities of each material. This adds to cotton’s usefulness in different settings, from sportswear to medical textiles.
Breathability
One of the main qualities of cotton is its breathability. Cotton fibers have a natural structure that lets air move freely through the fabric. This helps keep the wearer cool and comfortable in warm weather, as heat and moisture can escape more easily.
This feature also helps prevent skin irritation. Moisture is able to evaporate, reducing the chances of sweat building up on the skin. Because of this, cotton is often chosen for undergarments, T-shirts, and summer clothes.
In bedding and home textiles, breathable cotton helps create a fresher and more comfortable environment. Its ability to manage moisture and temperature makes it a favorite for sheets and pillowcases. Cotton’s breathability is key for comfort in both clothing and household uses.
Cotton Shrinkage: What You Need to Know
Does Cotton Shrink?
Yes, cotton does shrink, especially when exposed to heat and moisture. Understanding why and how cotton shrinks can help you prevent unwanted size changes.
Why Does Cotton Shrink?
Cotton shrinks because of the fiber’s natural structure. During manufacturing, cotton fibers are stretched and held under tension. When exposed to heat and water, these fibers relax and return to their natural state, causing the fabric to shrink.
When Does Cotton Shrink?
Cotton typically shrinks:
- First wash: Most shrinkage occurs during the first wash and dry cycle
- Hot water washing: Temperatures above 80°F increase shrinkage risk
- High heat drying: The dryer causes more shrinkage than washing
- Repeated cycles: Additional shrinkage may occur over multiple washes
Cotton Shrinkage by Type
| Cotton Type | Shrinkage Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 100% Cotton | 3-5% | Highest shrinkage |
| Cotton Blends | 1-3% | Less shrinkage due to synthetic fibers |
| Pre-shrunk Cotton | 1-2% | Treated to minimize shrinkage |
| Mercerized Cotton | 1-2% | Process reduces shrinkage |
| Sanforized Cotton | Under 1% | Pre-shrunk using special process |
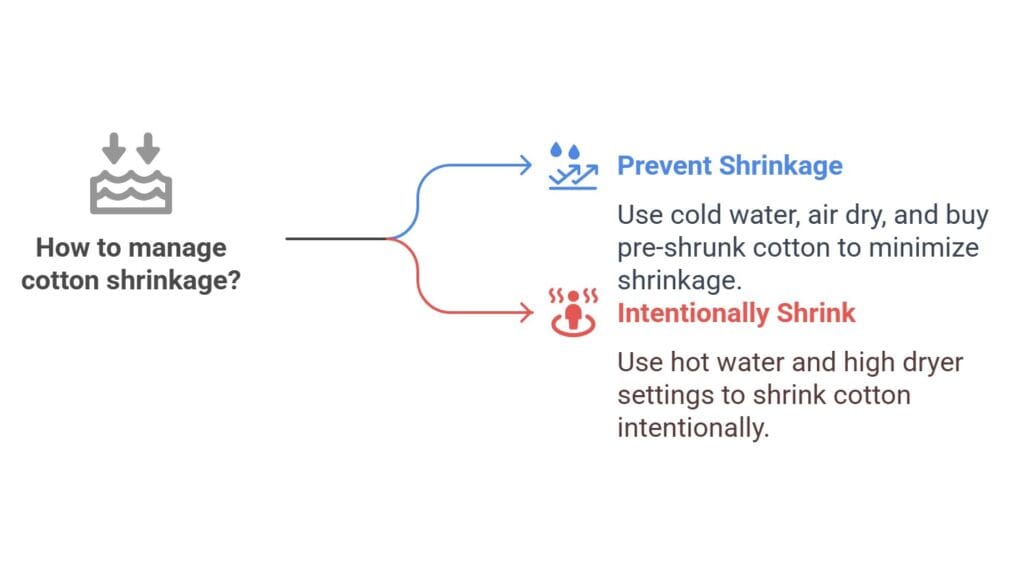
How to Prevent Cotton Shrinkage
- Wash in cold water (under 80°F)
- Air dry instead of using the dryer
- Use low heat if you must use the dryer
- Buy pre-shrunk cotton when possible
- Read care labels and follow instructions
How to Shrink Cotton Intentionally
How to shrink cotton or How to shrink a cotton shirt:
- Wash in hot water (above 130°F)
- Use the hottest dryer setting
- Leave in dryer longer than usual
- Repeat process if more shrinkage is needed
Can you shrink cotton? Yes, but it’s easier to shrink cotton than to unshrink it, so be careful with valuable items.
Common Uses Of Cotton Fabric
Cotton fabric has a wide range of uses in everyday life. It is popular for both home settings and personal clothing due to its comfort, durability, and ease of care.
Home Décor and Decorative Accents
Cotton is a common material in home décor because it is soft, breathable, and easy to clean. Many households use cotton for curtains and drapery, as it allows light to filter through while offering privacy.
It is also used in upholstery for sofas and chairs thanks to its durability and ability to hold color. Quilting and crafting projects often rely on cotton for its availability in many patterns and colors, making it easy to match or create decorative accents. Cotton is popular for tablecloths, placemats, cushion covers, and wall hangings.
Some families use cotton blankets and throws because they are lightweight and comfortable in many climates. Overall, cotton brings a combination of comfort and style into living spaces.
Clothing and Apparel
Cotton fabric is one of the most used materials in clothing. People choose it for everyday wear because it feels soft on the skin and allows air to pass through, which helps keep the body cool.
What is cotton used for? Cotton is found in t-shirts, socks, and underwear because it absorbs moisture and is gentle for sensitive skin. Many brands use cotton for jeans, dresses, and sleepwear due to its sturdiness and adaptability.
Some special types of cotton, like Egyptian cotton, are used to make high-quality shirts and luxury items. Cotton is also easy to wash and rarely causes skin irritation, making it a trusted fabric for families and children. In addition, cotton blends are popular in athletic and casual clothes for added stretch or durability.
Industrial and Technical Applications
Cotton isn’t just for clothing and home goods. It’s also used in:
- Medical supplies: Bandages, gauze, and surgical materials
- Canvas products: Tents, tarps, and outdoor gear
- Paper production: High-quality papers and currency
- Automotive: Tire cord and interior fabrics
- Filtration: Air and liquid filters
Get tailored fabric suggestions with our project-specific cotton recommendations tool that matches cotton types to your exact project needs.
Cotton Fabric For Furniture

Cotton fabric is widely used in furniture due to its breathable texture and easy maintenance. It comes in multiple forms, offering a range of choices for both aesthetics and function.
Upholstery and Slipcovers
Cotton is a popular choice for furniture upholstery and slipcovers because of its soft surface and natural look. Designers and homeowners often select cotton upholstery fabric for sofas, chairs, and ottomans. It is available in many colors, prints, and styles, making it simple to match different room designs.
Common types include cotton canvas fabric and pure cotton blends. Cotton canvas is thicker and offers a more durable feel, which works well for busy living spaces. Slipcovers made from cotton are straightforward to remove and machine-wash, adding to the fabric’s appeal for families or pet owners.
Cotton-based slipcovers give old furniture a fresh look without a major investment. Because cotton is a breathable fabric, it helps keep seating comfortable, especially in warmer climates. Some cotton upholstery fabrics are finished with stain-resistant treatments to help reduce spills and stains.
Durability In Furniture Applications
Cotton fabric has strengths and limits when used on furniture. It holds up well to gentle daily use but may show signs of wear over time, especially in high-traffic areas.
One key factor is weight. Heavier cotton, such as cotton canvas, is more durable and is often chosen for pieces that see frequent use. Lighter cottons can be suitable for accent chairs or decorative slipcovers but may not last as long under heavy use.
Maintenance is simple. Most cotton fabrics can be spot-cleaned or laundered, making them practical for homes with kids or pets. However, cotton is more likely to wrinkle and can fade if placed in direct sunlight for long periods.
Cotton vs Synthetic Upholstery Comparison:
| Feature | Cotton Canvas | Standard Cotton | Synthetic Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Thick | Medium | Varies |
| Durability | High | Moderate | Often higher |
| Best For | Heavy use | Light use | Heavy use |
| Washability | Good | Good | Often better |
| Breathability | Excellent | Excellent | Poor to moderate |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate | Varies |
Cotton’s straightforward care and comfort make it a common choice for many types of furniture, from sofas to slipcovers. Selecting the correct weight and finish can ensure better longevity and satisfaction.
Cotton Fabric In Crafting and Quilting

Cotton fabric is a favorite choice because it is durable, soft, and simple to sew. It is especially valued for its smooth texture and wide variety of prints, making it practical and reliable.
Quilting Projects
Cotton fabric is often used for quilting because it is easy to cut, press, and sew. Most quilting cotton is 100% cotton with a tight weave, which keeps stitches secure and minimizes fraying. It comes in many colors and patterns, helping quilters create designs that range from traditional to modern.
Quilters prefer cotton because it holds its shape well during piecing and quilting. Its breathability also means finished quilts are comfortable for everyday use. Popular projects using cotton include bed quilts, wall hangings, and quilted table runners.
Typical Quilting Cotton Qualities:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | 100% Cotton |
| Weave | Tight |
| Texture | Soft, not slippery |
| Shrinkage | Minimal if prewashed |
| Weight | Usually 4-6 oz per square yard |
| Width | Standard 44-45 inches |
Benefits For Crafts
Cotton fabric is very versatile in crafts. It can be used for making bags, appliqué, stuffed toys, and home décor items like curtains or pillow covers. The fabric is simple to handle, even for beginners, and can be cut or painted without losing its quality.
Crafters like cotton because it accepts dyes and markers well, making it easy to customize. Its strength holds up with repeated washing, which is important for items meant to last. Cotton is also less likely to irritate the skin, so it is safe for clothing and kid-friendly crafts.
Other benefits include affordability and the wide availability of patterns and solid colors. This allows crafters to easily match or coordinate materials within a project.
Cotton Fabric Pricing and Market Trends
Current Cotton Prices (2025)
Cotton prices fluctuate based on various factors including weather, global demand, and economic conditions. As of 2025, cotton prices have been influenced by:
- Supply chain challenges from weather events
- Increased demand for sustainable textiles
- Competition from synthetic alternatives
- Currency fluctuations in major producing countries
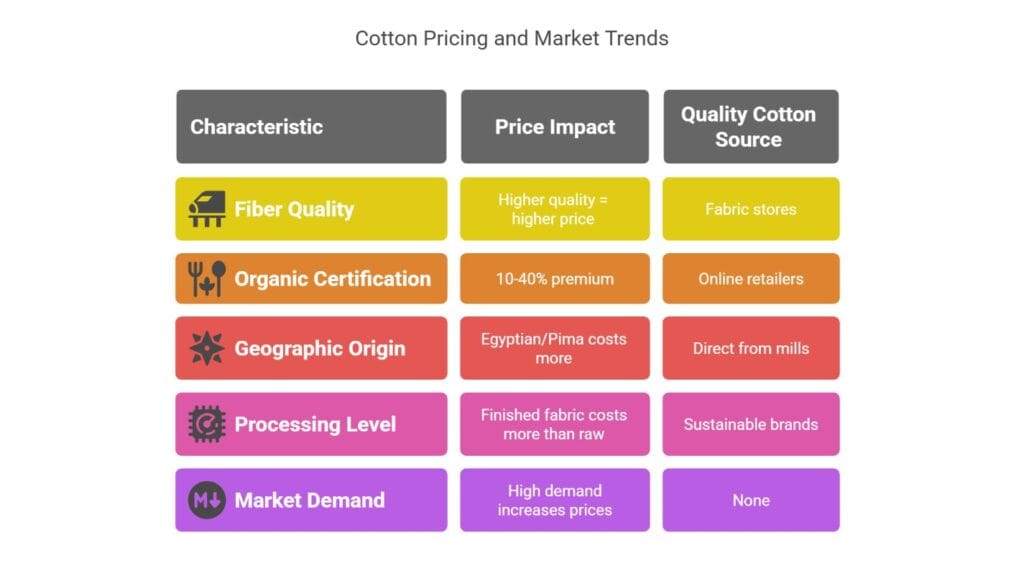
Price Factors
| Factor | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Fiber Quality | Higher quality = higher price |
| Organic Certification | 10-40% premium |
| Geographic Origin | Egyptian/Pima cotton costs more |
| Processing Level | Finished fabric costs more than raw cotton |
| Market Demand | High demand increases prices |
Where to Buy Quality Cotton
- Fabric stores: Best for seeing and feeling fabric quality
- Online retailers: Often better prices and selection
- Direct from mills: Bulk purchases for businesses
- Sustainable brands: Higher prices but better environmental practices
Cotton Biodegradability and Environmental End-of-Life
How Long Does Cotton Take to Decompose?
Pure cotton is fully biodegradable and typically decomposes within 1-5 months under proper composting conditions. Factors affecting decomposition time include:
- Fabric thickness: Thicker fabrics take longer
- Dyes and treatments: Chemical treatments slow decomposition
- Environmental conditions: Heat, moisture, and oxygen speed decomposition
- Soil microorganisms: More active bacteria means faster breakdown
Can You Compost Cotton Fabric?
Yes, you can compost cotton fabric, but there are important considerations:
Good for composting:
- 100% untreated cotton
- Natural dyed cotton
- Organic cotton without chemical finishes
Not suitable for composting:
- Cotton blends with synthetic fibers
- Chemically treated cotton (stain-resistant, etc.)
- Cotton with plastic buttons or zippers
Composting tips:
- Cut fabric into small pieces (2-3 inches)
- Remove any synthetic components
- Mix with brown materials (leaves, paper)
- Ensure proper moisture and air circulation
- Turn compost regularly
Cotton Care and Maintenance

Basic Cotton Care Guidelines
Proper care extends cotton’s life and maintains its appearance:
Washing:
- Use cold water (30°C/86°F or below)
- Turn garments inside out to protect colors
- Use gentle detergent without bleach
- Don’t overload the washing machine
Drying:
- Air dry when possible to prevent shrinkage
- If using a dryer, use low heat
- Remove while slightly damp to reduce wrinkles
- Shake out before hanging or folding
Ironing:
- Use medium heat setting
- Iron while slightly damp for best results
- Use steam for stubborn wrinkles
- Iron on the reverse side for dark colors
Stain Removal for Cotton
Cotton’s absorbent nature means it can stain easily, but it also responds well to treatment:
General stain removal:
- Treat stains immediately
- Blot, don’t rub
- Use cold water first
- Test treatments on hidden areas
Common stain solutions:
- Blood: Cold water and hydrogen peroxide
- Sweat: White vinegar and baking soda
- Oil: Dish soap applied directly
- Grass: Rubbing alcohol or enzyme detergent
For more detailed care instructions for different fabric types, check out our guides on washing and caring for various fabrics.
Cotton Fabric Technology and Innovation
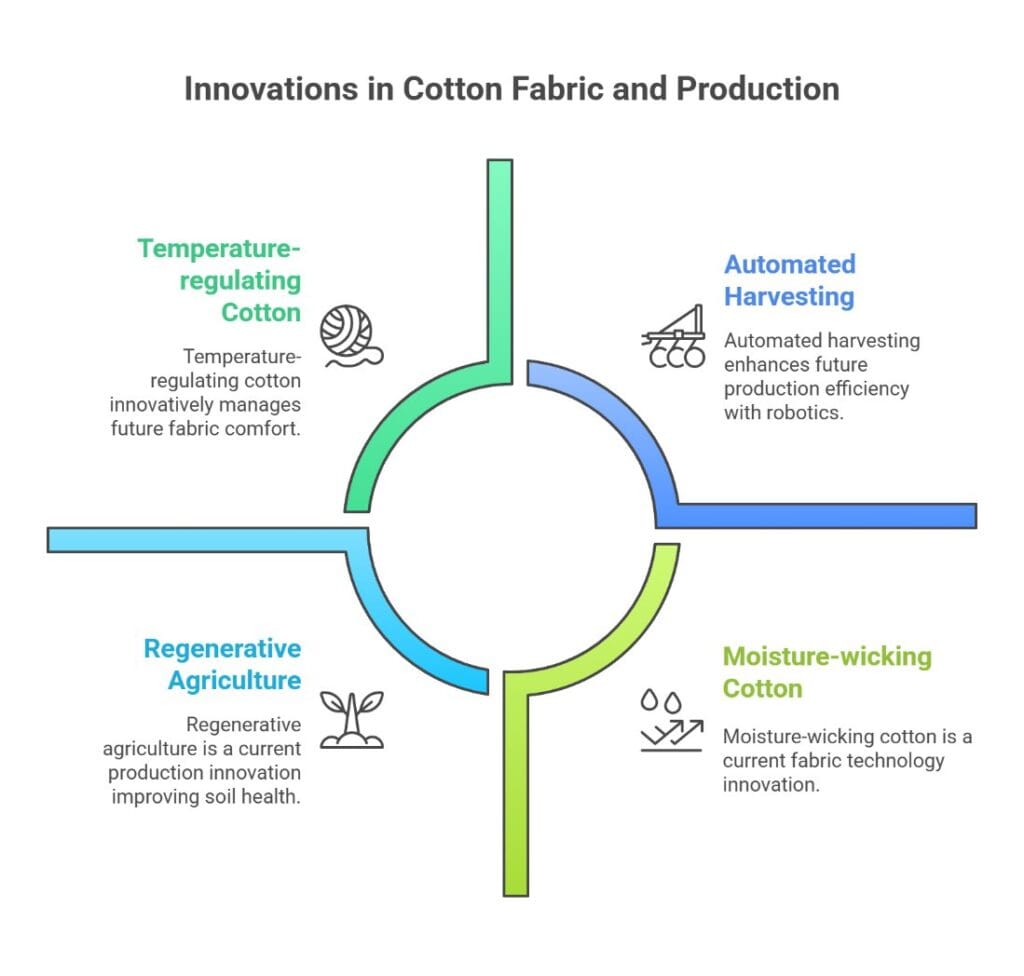
Smart Cotton Fabrics
The cotton industry is embracing technology with innovations like:
Moisture-wicking cotton: Special treatments that help cotton move sweat away from skin Antimicrobial cotton: Silver or copper treatments that resist bacteria and odors
Temperature-regulating cotton: Phase-change materials incorporated into cotton fibers Wrinkle-resistant cotton: Chemical treatments that maintain shape without ironing
Future of Cotton Production
Regenerative agriculture: Farming methods that improve soil health while growing cotton Blockchain traceability: Technology to track cotton from farm to finished product Water-efficient growing: New irrigation techniques and drought-resistant cotton varieties Automated harvesting: Robotics and AI to improve efficiency and reduce labor needs
Cotton vs Other Natural Fibers
Cotton vs Linen
| Aspect | Cotton | Linen |
|---|---|---|
| Softness | Soft from start | Gets softer with use |
| Wrinkles | Moderate wrinkling | Wrinkles easily |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
| Breathability | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Use our interactive fabric comparison tool to explore detailed comparisons between cotton, linen, hemp, and other natural fibers with customizable criteria for your specific needs
Cotton vs Hemp
Hemp is becoming more popular as a sustainable alternative. While hemp is more durable and eco-friendly, cotton remains softer and more versatile for different applications.
Cotton vs Bamboo
Bamboo fabric (actually bamboo rayon) is softer and more antibacterial than cotton, but the processing involves harsh chemicals that reduce its environmental benefits.
For a complete comparison of natural and synthetic options, see our comprehensive guide on natural vs synthetic fabrics.
Cotton Fabric Comparison Charts
Cotton Weight Classifications
| Weight Category | Ounces per sq yard | Grams per sq meter | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultra Light | 1-3 oz | 34-102 gsm | Voile, lawn, gauze |
| Light | 3-5 oz | 102-170 gsm | Poplin, broadcloth, quilting cotton |
| Medium | 5-8 oz | 170-271 gsm | Twill, sateen, medium canvas |
| Heavy | 8-12 oz | 271-407 gsm | Denim, duck cloth, heavy canvas |
| Extra Heavy | 12+ oz | 407+ gsm | Heavyweight canvas, workwear |
Use our fabric weight calculator to determine the ideal cotton weight for your specific project requirements
Cotton Thread Count Guide
| Thread Count | Quality Level | Best Uses | Feel |
|---|---|---|---|
| 150-200 | Basic | Everyday sheets, budget items | Rough, less durable |
| 200-400 | Good | Most bedding, mid-range clothing | Soft, comfortable |
| 400-600 | Very Good | Premium bedding, quality clothing | Very soft, smooth |
| 600-800 | Excellent | Luxury bedding, high-end clothing | Silky, luxurious |
| 800+ | Premium | Ultra-luxury items | Extremely soft |
Note: Thread count above 800 may use thinner, weaker fibers and isn’t always better quality.
Cotton Production and Global Impact
Major Cotton Producing Countries (2025)
| Country | Production (Million Bales) | % of World Production | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 26.5 | 22% | Largest producer and consumer |
| India | 24.5 | 20% | Mostly for domestic use |
| United States | 15.0 | 12% | High quality, mostly exported |
| Brazil | 12.5 | 10% | Growing sustainable practices |
| Pakistan | 8.5 | 7% | Major textile manufacturer |
| Others | 35.0 | 29% | Turkey, Australia, Uzbekistan, etc. |
Cotton’s Role in Global Economy
Cotton supports the livelihoods of over 250 million people worldwide and employs almost 7% of all labor in developing countries. The global cotton market is worth approximately $12 billion annually, with the textile industry adding significantly more value through processing and manufacturing.
Advanced Cotton Care Tips
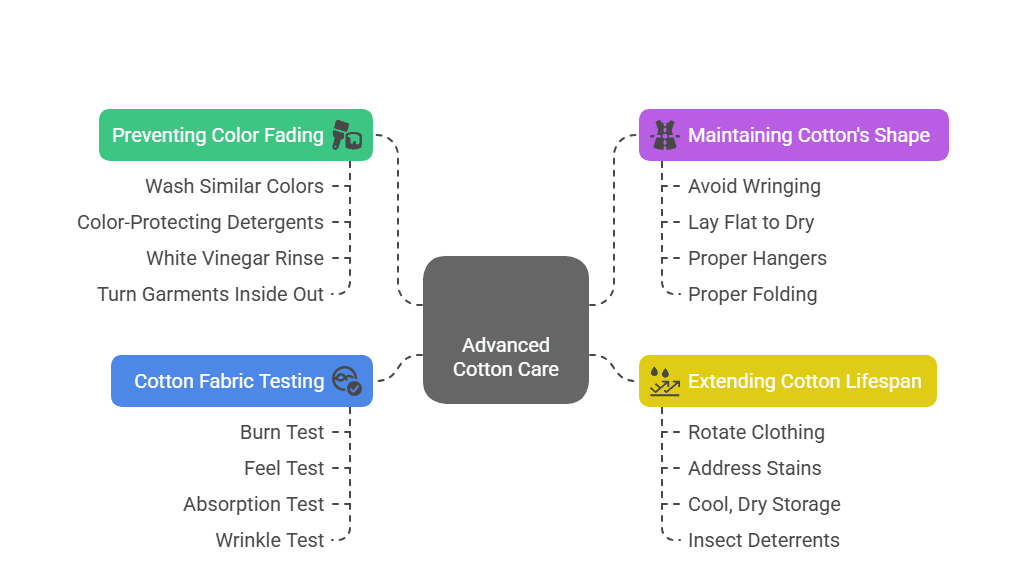
Professional Cotton Care Techniques
Preventing color fading:
- Wash similar colors together
- Use color-protecting detergents
- Add 1/2 cup white vinegar to rinse cycle occasionally
- Turn garments inside out before washing
Maintaining cotton’s shape:
- Don’t wring or twist wet cotton
- Lay flat to dry for knitted cotton items
- Use proper hangers for cotton shirts and dresses
- Store folded items properly to prevent creasing
Extending cotton lifespan:
- Rotate clothing regularly to reduce wear
- Address stains immediately
- Store in cool, dry places
- Use cedar blocks or lavender to deter insects
Cotton Fabric Testing
How to identify real cotton:
- Burn test: Cotton burns quickly with a yellow flame and smells like burning paper
- Feel test: Cotton feels soft and natural, not slippery like synthetic fabrics
- Absorption test: Cotton absorbs water quickly
- Wrinkle test: Cotton wrinkles more easily than synthetic blends
Sustainable Cotton Buying Guide
How to Choose Sustainable Cotton
Look for certifications:
- GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard): Ensures organic fibers and ethical manufacturing
- Better Cotton Initiative (BCI): Promotes water efficiency and worker welfare
- Cradle to Cradle: Considers entire lifecycle impact
- OEKO-TEX: Tests for harmful substances
Questions to ask retailers:
- Where was the cotton grown?
- What certifications does it have?
- How was the fabric processed?
- What is the company’s sustainability policy?
Sustainable cotton brands to consider:
- Patagonia (organic cotton commitment)
- Eileen Fisher (sustainable fiber sourcing)
- Pact (organic cotton basics)
- Kotn (Egyptian cotton with transparency)
Cost vs Value Analysis
| Cotton Type | Initial Cost | Durability | Environmental Cost | Overall Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | Low | Moderate | High | Low |
| Organic | Medium-High | Good | Low | High |
| Recycled | Medium | Good | Very Low | Very High |
| BCI | Low-Medium | Moderate | Medium | Medium-High |
While sustainable cotton may cost more upfront, it often provides better value through improved durability, comfort, and reduced environmental impact.
Cotton Industry Trends for 2025
Technology Integration
Digital printing: Advanced digital printing allows for more complex designs with less water usage than traditional methods.
AI quality control: Machine learning helps identify defects and quality issues in cotton processing.
Precision agriculture: GPS and sensor technology help farmers optimize water and fertilizer use.
Blockchain tracking: Some brands now offer complete supply chain transparency from farm to garment.
Market Predictions
Growing demand for:
- Organic and sustainable cotton
- Traceable supply chains
- Water-efficient production methods
- Recycled cotton content
Declining trends:
- Conventional cotton in premium markets
- Fast fashion cotton products
- Water-intensive production methods
- Unclear supply chain sourcing
Innovation Areas
New cotton varieties:
- Drought-resistant strains
- Naturally colored cotton (reducing dye needs)
- Improved fiber strength and length
- Disease-resistant plants
Processing improvements:
- Waterless dyeing technologies
- Enzyme-based processing (reducing chemicals)
- Closed-loop water systems
- Solar-powered manufacturing
Cotton Fabric Troubleshooting Guide
For instant solutions to cotton care issues, use our interactive cotton care troubleshooting guide for step-by-step problem diagnosis and solutions.
Common Cotton Problems and Solutions
Problem: Cotton shirts shrinking
- Solution: Pre-shrink fabric before sewing, wash in cold water, air dry or use low heat
Problem: Cotton fading quickly
- Solution: Turn inside out when washing, use cold water, avoid direct sunlight when drying
Problem: Cotton wrinkling excessively
- Solution: Remove from dryer while slightly damp, use fabric softener sparingly, iron with steam
Problem: Cotton feeling stiff after washing
- Solution: Use less detergent, add white vinegar to rinse cycle, avoid over-drying
Problem: Cotton pilling (small fiber balls)
- Solution: Turn inside out when washing, use gentle cycle, remove pills with fabric shaver
Cotton Fabric Storage Tips
Short-term storage (seasonal):
- Clean thoroughly before storing
- Store in breathable containers (cotton bags, not plastic)
- Add cedar blocks or lavender sachets
- Keep in cool, dry place
Long-term storage:
- Wash and completely dry items
- Use acid-free tissue paper for delicate items
- Check periodically for pests or moisture
- Refold occasionally to prevent permanent creases
Get customized storage recommendations for your climate and season with our seasonal cotton storage tips tool.
Regional Cotton Varieties and Characteristics
American Cotton Types
Upland Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum):
- Staple length: 26-32mm
- Characteristics: Strong, versatile, good for most applications
- Uses: General clothing, home textiles, industrial applications
Pima Cotton:
- Staple length: 32-35mm
- Characteristics: Extra soft, strong, lustrous
- Uses: Premium clothing, luxury bedding
Supima Cotton:
- Staple length: 35mm+
- Characteristics: Finest American cotton, certified quality
- Uses: High-end clothing, luxury goods
International Cotton Varieties
Egyptian Cotton:
- Staple length: 33-36mm
- Characteristics: Exceptionally long, strong, soft
- Uses: Luxury bedding, premium clothing
Sea Island Cotton:
- Staple length: 35-60mm
- Characteristics: Silky, extremely fine, rare
- Uses: Ultra-luxury textiles, specialty items
Organic Cotton (various origins):
- Characteristics: Grown without synthetic chemicals
- Benefits: Better for environment and sensitive skin
- Growing regions: Turkey, India, China, USA
Cotton Fabric Buying Checklist
Before You Buy
Determine your needs:
- ✅ Intended use (clothing, bedding, crafts)
- ✅ Required quantity
- ✅ Budget range
- ✅ Quality preferences
- ✅ Sustainability priorities
Calculate exactly how much fabric you need with our cotton fabric yardage calculator for quilting, clothing, and home décor projects.
Research the product:
- ✅ Cotton type and origin
- ✅ Weave and weight specifications
- ✅ Care requirements
- ✅ Certifications and standards
- ✅ Brand reputation
Check product details:
- ✅ Fabric composition (100% cotton vs. blend)
- ✅ Pre-shrunk status
- ✅ Colorfast testing results
- ✅ Thread count (for bedding)
- ✅ Return/exchange policy
Quality Indicators
Visual inspection:
- Even weave with no loose threads
- Consistent color throughout
- Clean, finished edges
- No stains or marks
Feel test:
- Appropriate softness for intended use
- Good hand feel (not too stiff or slippery)
- Adequate weight for purpose
- Smooth surface without rough patches
Economic Impact of Cotton Choices
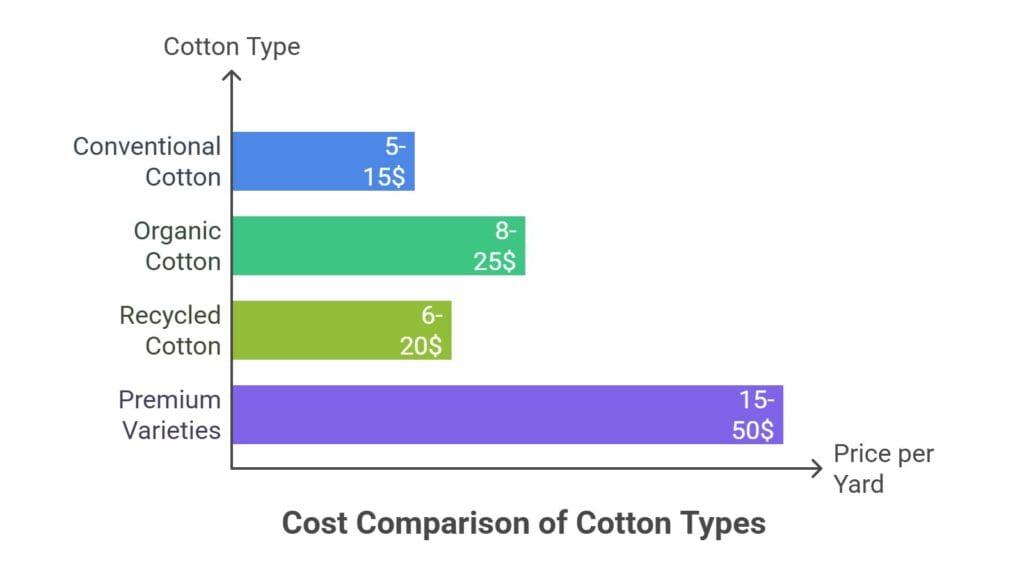
Cost Analysis: Conventional vs. Sustainable Cotton
Initial Purchase Price:
- Conventional cotton: $5-15 per yard
- Organic cotton: $8-25 per yard
- Recycled cotton: $6-20 per yard
- Premium varieties: $15-50 per yard
Lifetime Value Factors:
- Durability: Sustainable cotton often lasts 2-3x longer
- Performance: Better moisture management and comfort
- Resale value: Higher quality items retain value better
- Environmental cost: Avoiding future cleanup costs
Hidden costs of cheap cotton:
- Replacement frequency
- Environmental cleanup
- Health impacts from chemicals
- Social costs in producing regions
Professional Applications of Cotton
Medical and Healthcare Uses
Cotton’s natural properties make it ideal for medical applications:
- Absorbency: Wound dressings and bandages
- Sterilization compatibility: Can withstand high-temperature sterilization
- Hypoallergenic nature: Safe for sensitive skin
- Breathability: Surgical gowns and scrubs
Industrial Applications
Filtration: Cotton’s fiber structure makes it effective for air and water filtration systems.
Reinforcement: Cotton fibers strengthen composite materials in automotive and construction industries.
Paper production: High-quality papers and currency often contain cotton fibers for durability.
Canvas and technical textiles: Heavy-duty applications requiring strength and durability.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Cotton in Fashion History
Cotton has played a crucial role in fashion evolution:
- Industrial Revolution: Cotton mills drove technological advancement
- Colonial trade: Cotton shaped global commerce patterns
- Fashion democratization: Made fashionable clothing accessible to masses
- Modern sustainability: Leading the eco-fashion movement
Regional Cotton Traditions
Different regions have developed unique cotton traditions:
- India: Hand-spun khadi cotton representing self-reliance
- Egypt: Long-staple cotton prized since ancient times
- American South: Cotton’s complex historical and economic legacy
- West Africa: Traditional cotton cultivation and textile arts
Conclusion
Cotton fabric remains one of the world’s most important and versatile textiles, offering unmatched comfort, breathability, and adaptability across countless applications. From the softest baby clothes to the most durable canvas, cotton continues to be a fabric that meets both everyday needs and specialized requirements.
As we’ve explored throughout this comprehensive guide, cotton’s appeal lies not just in its natural properties but in its remarkable diversity. Whether you’re choosing Egyptian cotton for luxury bedding, organic cotton for environmental consciousness, or cotton canvas for heavy-duty projects, understanding the different types and qualities helps you make informed decisions.
The cotton industry is undergoing significant transformation as sustainability concerns drive innovation. The shift toward organic farming, water-efficient production methods, and recycled cotton represents a positive evolution that addresses environmental challenges while maintaining cotton’s beloved characteristics. Consumers increasingly have access to sustainable options that don’t compromise on quality or performance.
Key takeaways for cotton fabric users:
Choose quality over quantity: Investing in better cotton products often provides superior value through improved durability, comfort, and performance. Whether selecting natural vs synthetic fabrics, cotton’s natural benefits typically outweigh cost savings from synthetic alternatives.
Consider sustainability: Look for certifications like GOTS, BCI, or organic labels when possible. Sustainable cotton supports environmental health and often offers better working conditions for farmers and textile workers.
Proper care extends life: Following appropriate washing, drying, and storage guidelines significantly extends cotton’s lifespan. Using cold water, avoiding over-drying, and addressing stains promptly maintains cotton’s appearance and performance for years.
Match cotton type to purpose: Understanding the differences between cotton varieties helps optimize performance. Use lightweight cotton for summer clothing, heavyweight canvas for durability projects, and specialty cottons like Egyptian or Pima for luxury applications.
Embrace cotton’s versatility: From breathable fabrics for summer clothing to durable fabrics for everyday wear, cotton adapts to virtually any textile need.
The future of cotton looks promising as technology advances enable more sustainable production methods, improved fiber quality, and innovative applications. Smart cotton fabrics with moisture-wicking properties and antimicrobial treatments are expanding cotton’s utility, while regenerative agriculture practices are healing the land that grows our cotton.
Final recommendations:
For consumers, prioritize learning about cotton sources and production methods. Supporting brands committed to sustainable practices encourages positive industry changes. When possible, choose quality cotton products that will last longer and provide better value over time.
For businesses and manufacturers, investing in sustainable cotton sourcing not only meets growing consumer demand but often provides superior raw materials for better end products. Transparency in supply chains builds consumer trust and supports responsible industry practices.
Cotton fabric’s enduring popularity stems from its unique combination of comfort, versatility, and natural origin. As production methods continue improving and sustainable options become more accessible, cotton remains an excellent choice for countless applications. Whether you’re sewing your first quilt, choosing bedding for your family, or selecting fabrics for a business venture, cotton offers reliable performance backed by centuries of human use and continuous innovation.
By understanding cotton’s properties, environmental impact, and proper care requirements, you can make choices that benefit both your specific needs and the broader textile ecosystem. Cotton fabric truly represents the perfect balance of tradition and innovation, natural comfort and practical performance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cotton Fabric
What is another word for cotton fabric?
Cotton fabric may also be called cotton cloth, cotton textile, calico (for plain cotton), or by specific names like muslin, poplin, or canvas depending on the weave.
What is the proper name for cotton?
The scientific name for cotton is Gossypium, which refers to the genus of cotton plants. The most common species used for textile production are Gossypium hirsutum (upland cotton) and Gossypium barbadense (extra-long staple cotton).
What is the technical term for cotton?
In the textile industry, cotton may be referred to by its fiber classification, such as “staple fiber” (referring to its short, natural fiber length) or by its grade and quality designations.
Are there different types of cotton fabric?
Yes, there are many different types of cotton fabric, including:
• Weave types: Plain weave, twill, satin weave
• Fabric styles: Denim, corduroy, velvet, terry cloth
• Weight categories: Lightweight (lawn, voile), medium weight (poplin, broadcloth), heavyweight (canvas, duck)
• Finish types: Brushed (flannel), mercerized, sanforized
Does cotton stretch?
Pure cotton has minimal stretch, typically only 2-3% in any direction. However, cotton becomes more flexible when:
• Blended with stretchy fibers like spandex or elastane
• Knitted rather than woven (jersey cotton has more stretch)
• Cut on the bias (diagonal grain has more give)
What does cotton look like?
Raw cotton appears as fluffy, white or cream-colored fibers attached to seeds in cotton bolls. Cotton fabric has a matte finish (unlike synthetic fabrics), feels soft and slightly textured, and has visible fiber ends when examined closely.
How to make cotton fabric?
Cotton fabric production involves several steps:
1. Harvesting: Cotton bolls are picked from plants
2. Ginning: Seeds are removed from fibers
3. Carding: Fibers are aligned and cleaned
4. Spinning: Fibers are twisted into yarn
5. Weaving or knitting: Yarn is made into fabric
6. Finishing: Fabric is dyed, printed, or treated
What is cotton used for?
Cotton is used in numerous applications:
• Clothing: T-shirts, jeans, underwear, socks, dresses
• Home textiles: Bed sheets, towels, curtains, upholstery
• Medical: Bandages, gauze, surgical materials
• Industrial: Canvas, rope, paper, filters
• Personal care: Cotton balls, swabs, pads