From Basic Comfort to Smart Technology: Your Complete 2025 Guide to Stretch Fabric Types, Testing Standards, and Sustainable Innovations
Stretchy fabrics have completely changed how we think about clothing comfort and performance. These innovative textiles, which contain elastic fibers like lycra, spandex, or elastane, can conform to our bodies while allowing complete freedom of movement. Stretch fabrics offer the perfect balance of snug fit and exceptional comfort, making them ideal for everything from athletic wear to everyday clothing.
The versatility of stretch fabrics extends far beyond just activewear. With their ability to mold to body contours without sacrificing comfort, these fabrics have found their way into nearly every clothing category. The addition of elastic components creates textiles that move with us rather than against us, enhancing both functionality and wearability.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Stretch fabrics blend comfort and functionality by conforming to the body while allowing freedom of movement
- The global stretch fabric market was valued at USD 596.67 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1079.23 billion by 2030
- Modern stretch textiles incorporate sustainable materials and smart technology features
- Understanding stretch percentages and fabric types helps you choose the right material for your needs
Understanding Stretchy Fabrics
Stretchy fabrics have revolutionized the clothing industry by combining comfort with functionality. These innovative textiles use special fibers and construction methods to create materials that move with our bodies.
What Kind of Fabric is Stretchy?
Several types of fabrics offer stretch properties:
Synthetic Stretch Fabrics:
- Spandex/Lycra/Elastane blends (most common)
- Polyester with elastane
- Nylon with spandex
- Acrylic blends
Natural Stretch Options:
- Cotton-elastane blends
- Bamboo with spandex
- Modal-elastane combinations
- Wool jersey (mechanical stretch)
Construction-Based Stretch:
- Jersey knits
- Rib knits
- Ponte knits
- Double knits
Components of Stretch
The magic of stretch fabrics comes from their composition. Most stretchy fabrics contain elastane, also known as spandex or Lycra, which provides the stretching capability.
Elastane fibers can stretch to 5-8 times their original length and snap back to their original shape. These powerful fibers are rarely used alone – they’re typically blended with other materials like cotton, polyester, or nylon.
Elastane Percentage Guidelines:
- 2-3% elastane: Light stretch for comfort
- 5-10% elastane: Moderate stretch for activewear
- 15-20% elastane: High stretch for performance garments
- Up to 20% elastane: Maximum stretch for specialized applications
Is 100% Polyester Stretchy?
No, 100% polyester is not naturally stretchy. Pure polyester fibers are strong and durable but lack elasticity. However, polyester becomes stretchy when:
- Blended with elastane (even 2-5% makes a significant difference)
- Knitted in specific constructions that provide mechanical stretch
- Processed with special texturing techniques
Common Polyester Stretch Blends:
- 95% polyester, 5% elastane: Good stretch for activewear
- 92% polyester, 8% elastane: Excellent stretch and recovery
- 70% polyester, 30% other fibers: May have moderate stretch depending on blend
What Fabrics Are 4-Way Stretch?
Four-way stretch fabrics extend both horizontally and vertically, providing maximum mobility. Common 4-way stretch fabrics include:
- Spandex blends (highest stretch capability)
- Performance jerseys with elastane
- Athletic mesh fabrics
- Compression fabrics for sportswear
- Stretch denim with elastane
- Ponte knits with spandex
Two-way stretch fabrics only extend in one direction (usually horizontally), while four-way stretch materials extend both horizontally and vertically for maximum mobility.
Types of Stretchy Fabrics

Several types of stretchy fabrics serve different purposes in our wardrobes. Understanding these differences helps with choosing the right fabric for specific needs.
Lightweight Stretch Fabrics
Jersey is a lightweight knit with natural stretch that’s perfect for t-shirts and casual dresses. It typically contains cotton blended with elastane or polyester.
Stretch Cotton Blends preserve all the positive properties of cotton fabric: breathability, water-absorbing function, and hypoallergenic qualities while adding comfort stretch.
Modal and Bamboo Blends offer soft, stretchy alternatives with moisture-wicking properties and natural antibacterial benefits.
Performance Stretch Fabrics
Lycra (a brand name for elastane) blended fabrics offer excellent recovery and are ideal for swimwear and activewear. They maintain their shape even after repeated stretching.
Nylon-spandex blends create lightweight, moisture-wicking fabrics that excel in athletic wear. They offer excellent durability and stretch with superior color retention.
Compression fabrics provide targeted support for muscles while maintaining flexibility for athletic performance.
Heavy Stretch Fabrics
Neoprene provides structured stretch with insulating properties, commonly used in wetsuits and technical clothing. This thick, stretchy fabric offers excellent compression and temperature regulation.
Ponte knit combines rayon, polyester, and spandex for a stable stretch fabric that’s perfect for pants and structured garments. It maintains its shape while providing comfort.
Stretch denim incorporates elastane into traditional cotton denim, creating jeans that move with your body while maintaining the classic denim look.
Which Fabric is Soft and Stretchable?
The softest stretchable fabrics include:
- Bamboo-spandex blends – Incredibly soft with natural moisture-wicking
- Modal-elastane combinations – Silky smooth feel with good stretch
- Cotton-lycra jersey – Familiar cotton softness with added stretch
- Microfiber blends – Ultra-soft synthetic feel
- Viscose-elastane – Smooth, flowing fabric with moderate stretch
Market Size and Industry Growth
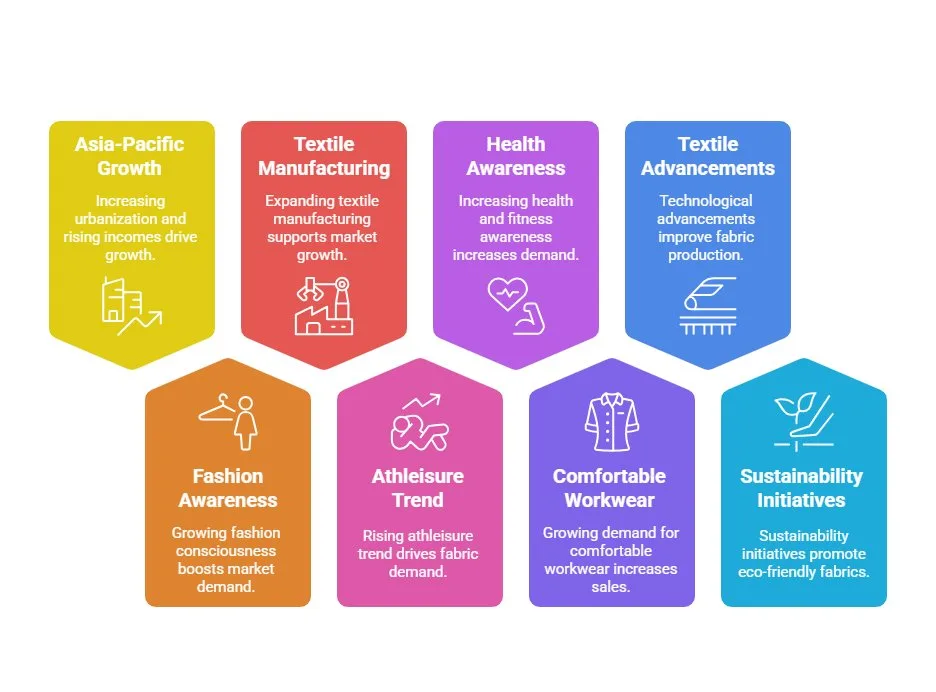
The stretch fabric industry has experienced remarkable growth, driven by increasing demand for comfort and performance in clothing.
Global Market Statistics
The global stretch fabric market was valued at USD 596.67 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 1079.23 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 7.44%. This growth reflects the increasing consumer preference for comfortable, functional clothing.
The spandex fabric market specifically is expected to grow from USD 9.1 billion in 2023 to USD 20.2 billion by 2031, showing the strong demand for high-performance stretch materials.
Regional Market Trends
North America and Europe dominate as major markets for stretch fabrics, driven by established fashion brands and high consumer demand for performance apparel.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing market, fueled by:
- Increasing urbanization
- Rising disposable incomes
- Growing fashion consciousness
- Expanding textile manufacturing capabilities
Market Drivers
Key factors driving market growth include:
- Rising athleisure trend
- Increasing health and fitness awareness
- Growing demand for comfortable workwear
- Technological advancements in textile manufacturing
- Sustainability initiatives in fashion
Technical Testing Standards and Quality Assurance
Understanding fabric testing standards helps ensure quality and performance in stretch textiles.
Industry Testing Standards
ASTM D6614/D6614M-20 is the standard test method for stretch properties of textile fabrics using the Constant Rate of Extension (CRE) method. This test determines the stretch and growth properties that garments may exhibit during use.
Professional textile testing follows established protocols set by ASTM International, the global leader in testing standards. According to ASTM D6614, the standard test method for stretch properties determines how garments will perform during actual use, providing manufacturers and consumers with reliable quality metrics.
ASTM D3107 covers stretch properties of fabrics woven from stretch yarns, specifically for fabrics with high stretch (greater than 12%) and good recovery properties.
ASTM D2594 measures stretch properties of knitted fabrics having low power, essential for evaluating comfort stretch in everyday garments.
Quality Testing Parameters
Professional testing evaluates:
- Stretch percentage at various loads
- Recovery properties after stretching
- Growth resistance over time
- Durability through repeated cycles
- Dimensional stability after washing
Performance Metrics
Quality stretch fabrics should demonstrate:
- Consistent stretch in both directions (for 4-way stretch)
- 90%+ recovery to original dimensions
- Minimal growth after 50+ stretch cycles
- Resistance to pilling and snagging
- Colorfastness through washing and wear
Smart Textiles and Future Innovations

The integration of technology with stretch fabrics represents the next frontier in textile innovation.
Smart Stretch Fabrics
The smart textiles market reached USD 4.9 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 28.5 billion by 2033, with stretch fabrics playing a crucial role in this growth.
Smart stretch fabrics now incorporate:
- Conductive yarns for health monitoring
- Temperature-responsive fibers that adjust to body heat
- Moisture sensors for performance tracking
- LED integration for safety and aesthetics
- Compression technology that adapts to activity level
Emerging Technologies
Phase Separation-Enabled Ambient (PSEA) Spinning allows creation of strong, stretchable, and electrically conductive fibers at room temperature, inspired by spider silk production.
Self-healing fabrics can repair minor tears and maintain stretch properties over extended use periods.
Bio-responsive materials adjust their properties based on environmental conditions like humidity, temperature, or pH levels.
Military and Technical Applications
The smart textiles military market is projected to reach USD 3.34 billion by 2033, growing at 26.14% CAGR. Applications include:
- Temperature monitoring and control systems
- Health monitoring capabilities
- Enhanced protection and mobility
- Energy harvesting technologies
- Communication integration
Environmental Impact and Sustainability

Understanding the environmental implications of stretch fabrics helps make informed choices about textile consumption.
Microplastics Concerns
Synthetic stretch fabrics contribute to microplastic pollution through fiber shedding during washing. Key facts:
- 35% of global microplastic pollution comes from washing synthetic textiles
- Synthetic fibers account for 60% of global fiber production
- 13,000 tonnes of textile microfibers are released to European surface water annually
- Microfibers can accumulate in the food chain and affect marine ecosystems
Research from the European Environment Agency confirms that approximately 13,000 tonnes of textile microfibers are released to European surface waters annually, representing 8% of total primary microplastic releases. This comprehensive study highlights the urgent need for sustainable alternatives and improved washing practices to reduce environmental impact.
Factors Affecting Microfiber Release
Washing conditions significantly impact fiber shedding:
- Long wash cycles increase wear and tear
- High temperatures damage fabric structure
- Washing powder creates more abrasion than liquid detergent
- Top-loading machines cause more shedding than front-loading models
- Fabric softener reduces friction and fiber damage
Solutions and Best Practices
Washing Machine Filters:
- Lint LUV-R filters reduce microfibers by 87%
- CoraBall devices reduce shedding by 26%
- Built-in washing machine filters becoming mandatory in some regions
Consumer Actions:
- Wash clothes less frequently
- Use full loads to reduce friction
- Choose cold water washing
- Use gentle cycles for synthetic garments
- Consider washing bags for synthetic items
Sustainable Alternatives
Natural Stretch Options:
- Mechanical stretch from cotton knits
- Wool jersey with natural elasticity
- Bamboo and modal blends
- Hemp-cotton combinations
Recycled Materials:
- Recycled polyester with spandex
- Post-consumer elastane recovery
- Bio-based polyester alternatives
- Circular economy textile programs
Biodegradable Innovations:
- Plant-based elastomers
- Compostable stretch fibers
- Chemical-free processing methods
- Sustainable dyeing techniques
Evaluating Fabric Characteristics
When choosing stretchy fabrics for comfort, it’s important to assess several key properties that determine performance in real-world conditions.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Breathability is crucial for comfort in stretchy fabrics. Test breathability by holding fabric up to a light source – more visible light often indicates better air permeability.
Cotton-spandex blends offer good breathability while maintaining stretch. Pure cotton knits provide comfort stretch through construction rather than elastic fibers.
For moisture management, test how quickly fabric wicks away moisture. Place a drop of water on the fabric and time how long it takes to spread out. Faster spreading typically indicates better wicking properties.
Quick breathability test: Stretch the fabric over your hand and blow through it. The easier you can feel air passing through, the more breathable it is.
Weight and Comfort Level
Fabric weight significantly impacts overall comfort:
- Lightweight fabrics (under 200 g/m²): Ideal for high mobility and warm conditions
- Medium-weight fabrics (200-300 g/m²): Good balance between support and comfort for everyday wear
- Heavy fabrics (over 300 g/m²): Provide structure but may restrict movement
When evaluating comfort, consider how fabric feels against skin. Run it along your inner arm where skin is sensitive. The fabric should feel smooth without irritation.
Stretch percentage matters for comfort: 20-30% stretch with excellent recovery provides optimal comfort for most applications.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Durability determines how long garments maintain their shape and function. Fabrics with high tenacity yarns last longer under repeated stretching.
To test resilience, stretch fabric and hold for 30 seconds. Quality stretch fabrics should return to original shape without bagging or sagging.
Durability indicators:
- Tight, even weave or knit structure
- Smooth, consistent stretch in all directions
- No visible thinning when stretched
- Minimal pilling when rubbed with a textile brush
Applications of Stretchy Fabrics

Stretchy fabrics have transformed many sectors with their unique blend of comfort and functionality.
Activewear and Performance Gear
Activewear relies heavily on stretch fabrics for good reason. These materials move with the body during exercise, preventing restriction and allowing full range of motion. Performance fabrics wick moisture away from skin, keeping wearers dry during intense activities.
Many performance fabrics contain spandex or elastane blended with polyester or nylon. This combination creates lightweight, durable clothing that returns to its original shape after stretching.
Popular activewear applications:
- Compression leggings and shorts
- Sports bras and supportive tops
- Swimming suits and competitive swimwear
- Yoga pants and fitness shorts
- Dance and gymnastics wear
The flexibility of these fabrics makes them perfect for activities requiring extensive movement.
Everyday Comfort Wear
Stretch fabrics have revolutionized everyday clothing, making comfort a priority without sacrificing style. Jeans with added elastane now offer the classic denim look with significantly improved comfort and fit.
Many brands now incorporate stretch into business attire. Dress shirts, slacks, and even suits contain small percentages of elastic fibers, allowing freedom of movement during long workdays.
Undergarments have dramatically improved with stretch technology. Modern underwear, bras, and shapewear use stretchy fabrics to provide support while remaining comfortable all day.
Maternity wear relies heavily on stretch fabrics to accommodate changing body shapes while maintaining comfort and style throughout pregnancy.
Specialized Industrial and Medical Use
Beyond fashion, stretch fabrics serve crucial functions in specialized applications.
Medical Applications:
- Compression garments for circulation improvement
- Surgical gloves with enhanced dexterity
- Patient positioning aids
- Therapeutic support garments
Workwear Applications: The stretch workwear fabrics market was valued at $2.3 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach $4.4 billion by 2032. Applications include:
- Construction worker uniforms with mobility panels
- Healthcare scrubs with comfort stretch
- Manufacturing uniforms with flexibility zones
- First responder gear with stretch inserts
Technical and Safety Applications:
- Military uniforms with stretch panels at joints
- Protective workwear with mobility enhancement
- Technical gloves for detailed work
- Safety gear with comfort improvements
Fabric Composition Analysis

Understanding specific fabric compositions helps in selecting the right material for different applications.
Does 100% Cotton Stretch?
Pure 100% cotton does not naturally stretch. However, cotton can have mechanical stretch when:
- Knitted in jersey or rib constructions
- Woven with specific weave patterns
- Pre-treated with mechanical processes
Most comfortable cotton garments include 2-5% elastane for added stretch and shape retention.
Is Viscose Fabric Stretchy?
Pure viscose is not inherently stretchy like spandex, but it can have slight natural stretch due to its fiber structure. Viscose becomes more stretchy when:
- Blended with elastane (common in 95% viscose, 5% spandex blends)
- Knitted rather than woven
- Treated with stretch-enhancing finishes
The stretch amount varies based on fabric weave, blend composition, and manufacturing treatments.
Is Lyocell Stretchy?
Lyocell (such as Tencel) has minimal natural stretch on its own. However, it becomes stretchy when:
- Blended with elastane or spandex
- Knitted in stretchy constructions
- Combined with other elastic fibers
Lyocell-elastane blends offer excellent drape, moisture management, and comfort stretch.
Understanding Elastane Percentages
Is 2% Elastane Stretchy? Yes, even 2% elastane provides noticeable stretch and improved comfort. This low percentage offers:
- Light stretch for ease of movement
- Better shape retention
- Improved fit without being overly clingy
Is 95% Polyester 5% Elastane Stretchy? Yes, this is a highly stretchy combination. The 5% elastane provides:
- Excellent stretch and recovery
- Ideal for activewear and fitted garments
- Good shape retention after washing
- Suitable for high-movement activities
Is 92% Polyester and 8% Elastane Stretchy? Yes, 8% elastane creates very stretchy fabric with:
- Superior stretch capability
- Excellent recovery properties
- High performance for athletic wear
- Strong shape retention over time
Care and Maintenance
Proper care extends the life of stretch fabrics and maintains their performance properties.
Washing Guidelines
Temperature considerations:
- Use cold water (30°C or below) to prevent elastane degradation
- Hot water can break down elastic fibers
- Gentle cycles reduce mechanical stress
Detergent selection:
- Liquid detergents are gentler than powder
- Avoid bleach and fabric softeners with elastane
- Use detergents designed for stretch fabrics when available
Drying Best Practices
Air drying is preferred for stretch fabrics:
- Lay flat to prevent stretching
- Avoid direct sunlight which can degrade elastane
- Hang carefully to prevent distortion
Machine drying considerations:
- Use low heat settings only
- Remove while slightly damp
- Avoid over-drying which makes fabrics stiff
Storage and Care
- Fold rather than hang heavy stretch garments
- Store in cool, dry places
- Avoid extreme temperatures
- Rotate garments to prevent constant stress on fibers
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best natural stretchy fabric?
Cotton jersey and wool jersey offer the best natural stretch through their knitted construction. For blended options, cotton-elastane and bamboo-spandex combinations provide excellent natural feel with added stretch.
Which fabric is known for its ability to stretch?
Spandex (also called Lycra or elastane) is the fabric most known for its stretching ability. It can stretch up to 400% of its original size and maintains excellent recovery properties.
What material has the most stretch?
Pure spandex has the most stretch capability, extending up to 8 times its original length. However, in practical applications, spandex blends with 15-20% spandex content offer the highest functional stretch.
What is stretchy fabric called?
Stretchy fabrics are called by several names:
• Stretch fabric
• Elastic fabric
• Spandex blend
• Lycra blend
• Elastane blend
• Performance fabric
• Comfort stretch fabric
What fabric is thin and stretchy?
Thin, stretchy fabrics include:
• Stretch mesh
• Lightweight jersey
• Stretch chiffon
• Performance microfiber
• Stretch silk blends
• Athletic moisture-wicking fabrics
What material is stretchy and shiny?
Materials that are both stretchy and shiny include:
• Stretch satin
• Metallic spandex blends
• Stretch vinyl or leather
• Performance fabrics with metallic threads
• Stretch sequined fabrics
• Lycra with metallic finishes
Are there natural stretchy fabrics?
Yes, several natural options provide stretch:
• Cotton jersey (mechanical stretch)
• Wool jersey and knits
• Bamboo knits
• Hemp-cotton blends
• Linen-cotton jersey combinations
What stretchy fabric doesn’t fray?
Knitted stretch fabrics typically don’t fray because of their loop construction:
• Jersey knits
• Rib knits
• Interlock knits
• Double knits
• Stretch fleece
Which is better: 2-way or 4-way stretch fabric?
4-way stretch is generally better for:
• Athletic wear and activewear
• Fitted garments requiring maximum mobility
• Garments worn during physical activity
2-way stretch works well for:
• Casual everyday wear
• Garments needing stretch in one direction only
• Cost-effective comfort applications
Innovations in Stretchy Fabrics

The fabric industry continues advancing with exciting innovations focused on performance, sustainability, and smart technology integration.
Advanced Manufacturing Processes
4-Way Stretch Technology represents a major advancement in fabric engineering. Unlike traditional stretch materials that extend in one direction, 4-way stretch expands both horizontally and vertically, creating more natural movement patterns.
Modern manufacturing uses specialized machinery that can incorporate elastane fibers during weaving or knitting processes. Some manufacturers use natural stretch technology which creates stretch in 100% cotton without elastomeric yarns.
Heat-setting processes stabilize stretch properties, ensuring fabrics return to original shape after stretching. Digital knitting and performance finishing treatments add functionality like moisture-wicking or compression capabilities.
Water Repellent Technologies
Modern stretchy fabrics now incorporate impressive water resistance capabilities. Durable Water Repellent (DWR) treatments create hydrophobic surfaces that make water bead up and roll off instead of soaking in.
This innovation means comfortable stretch clothing can be worn in light rain without getting soaked. The technology works by coating fabric fibers with molecular structures that repel water molecules.
The best water-repellent stretch fabrics maintain breathability while keeping moisture out. This balance is crucial for athletic performance, allowing sweat vapor to escape while blocking external moisture.
Sustainable Innovations
The textile industry is developing eco-conscious alternatives to traditional stretchy materials. Many standard stretch fabrics rely on elastane (spandex), which has significant environmental impact.
Natural Stretch Technology uses cotton fibers without spandex, creating stretch through special weaving techniques. This mechanical stretch approach reduces reliance on synthetic materials.
Biodegradable Options include:
- Plant-based elastomers replacing petroleum-derived elastane
- Recycled polyester with natural rubber components
- Fabrics using naturally stretchy fibers like wool blended with sustainable synthetics
- Bio-based polyester alternatives that maintain stretch properties
These innovations provide expected comfort and performance while reducing environmental impact.
Future Trends in Stretchy Fabrics
The stretch fabric industry continues evolving with technological advancements and sustainability becoming increasingly important.
Technology Integration
Smart Textile Integration represents the future of stretch fabrics. Advanced materials will incorporate sensors, conductive yarns, and responsive coatings while maintaining stretch properties. These fabrics will monitor vital signs, track performance, and adjust to environmental conditions.
Adaptive Materials will respond to stimuli like temperature, moisture, or pressure. Fabrics will automatically adjust compression levels, breathability, or insulation based on activity and environmental needs.
Sustainability Focus
Circular Economy Approaches are reshaping production:
- Recycled elastane using post-consumer materials
- Biodegradable elastane that breaks down naturally
- Bio-based elastane derived from plant sources
- Closed-loop recycling systems for stretch fabrics
Environmental Responsibility drives innovation in:
- Water conservation in dyeing and finishing
- Reduced chemical usage in processing
- Energy-efficient manufacturing processes
- End-of-life disposal solutions
Market Evolution
Customization Technology will enable:
- 3D printing of stretch fabrics
- On-demand manufacturing
- Personalized stretch characteristics
- Local production reducing transportation impact
Performance Enhancement continues advancing:
- Superior moisture management
- Enhanced durability and longevity
- Improved stretch and recovery properties
- Better integration with smart technologies
Conclusion
Stretchy fabrics have fundamentally transformed the textile industry, evolving from specialized athletic wear to essential components in virtually every category of clothing and technical applications. With the global stretch fabric market projected to nearly double from USD 596.67 billion in 2023 to USD 1079.23 billion by 2030, these materials represent one of the fastest-growing segments in textiles.
The success of stretch fabrics lies in their ability to balance multiple priorities: comfort, performance, durability, and increasingly, sustainability. From the basic cotton-elastane blends that revolutionized everyday wear to advanced smart textiles that monitor health metrics, these materials continue pushing the boundaries of what fabric can accomplish.
Key Takeaways and Recommendations
For Consumers:
- Choose stretch fabrics with 2-5% elastane for everyday comfort, 5-10% for activewear, and 15-20% for high-performance applications
- Consider environmental impact by selecting natural fiber blends when possible and following proper care guidelines to extend garment life
- Use washing machine filters and gentle care practices to reduce microfiber pollution
- Look for quality certifications like Oeko-Tex when purchasing stretch garments
For Industry Professionals:
- Understand ASTM testing standards (D6614, D3107, D2594) to ensure consistent quality and performance
- Stay current with smart textile innovations and sustainable material developments
- Consider the entire lifecycle impact of stretch fabrics, from production to disposal
- Invest in technologies that reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance
For the Future: The integration of smart technology with stretch fabrics represents the next major evolution in textiles. As the smart textiles market grows from USD 4.9 billion to USD 28.5 billion by 2033, we can expect stretch fabrics to play an increasingly important role in health monitoring, performance optimization, and environmental adaptation.
Sustainability challenges, particularly microplastic pollution from synthetic stretch fabrics, require continued innovation in biodegradable alternatives and circular economy approaches. The development of plant-based elastomers and mechanical stretch technologies offers promising paths toward more sustainable stretch fabric solutions.
Final Recommendations:
- Prioritize quality over quantity – well-made stretch garments last longer and perform better
- Understand fabric composition – knowing elastane percentages helps predict performance and care requirements
- Practice responsible care – proper washing and drying extends fabric life and reduces environmental impact
- Stay informed about innovations – new technologies continue improving performance while reducing environmental impact
- Consider the full lifecycle – from raw materials to disposal, make choices that support sustainable practices
The future of stretch fabrics looks bright, with continued innovation in performance, sustainability, and smart technology integration. As consumers become more conscious of environmental impact and demand higher performance from their clothing, stretch fabrics will continue evolving to meet these needs while maintaining the comfort and functionality that made them indispensable in modern wardrobes.
Whether you’re selecting stretch fabrics for athletic performance, everyday comfort, or specialized applications, understanding the science, sustainability, and future trends of these remarkable materials empowers better decision-making for both personal use and professional applications. The stretch fabric revolution is far from over, and the innovations ahead promise even more exciting developments in this dynamic field.

