Breathability, Durability, and Sustainability: Choosing Fabrics That Match Your Lifestyle
Choosing the right fabric for your clothes affects both comfort and function. Natural fibers from plants and animals like cotton and wool offer breathability and softness, while synthetic fibers made from chemical compounds provide durability and easy care.
Different fabric types serve different purposes in your wardrobe. A cotton t-shirt keeps you cool on hot days, while a synthetic workout shirt wicks away sweat during exercise. Many modern clothes blend both types to combine their best qualities.
Your fabric choices impact more than just comfort. The materials in your clothes affect the environment, your skin’s health, and how long the garments last. Understanding these differences helps you make smart decisions when buying new clothes.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Natural and synthetic fabrics each have unique benefits that make them suitable for different uses
- Modern textile technology combines both fiber types to create improved performance fabrics
- Your choice of fabric affects comfort, durability, and environmental impact
- Smart fabrics and sustainable innovations are revolutionizing the textile industry in 2025
Historical Development of Natural and Synthetic Fabrics
Before the 20th century, you would have only found natural fibers like cotton, wool, silk, and linen in clothing and textiles. These materials came from plants and animals through simple mechanical processing.
Trade routes played a key role in spreading natural fabrics across cultures. You could find silk moving from China to Europe, while cotton spread from India to other regions.
A major change happened in 1935 when scientists created the first true synthetic fabric. DuPont developed nylon, marking the start of the synthetic fabric era.
Today, you can choose from many synthetic options. Polyester offers durability and easy care. Rayon combines natural and artificial materials. Acrylic provides a wool-like feel at a lower cost.
Natural Fabrics
- Cotton: Breathable and soft
- Wool: Warm and moisture-wicking
- Silk: Smooth and luxurious
- Linen: Cool and durable
Synthetic Fabrics
- Nylon: Strong and elastic
- Polyester: Wrinkle-resistant
- Rayon: Silk-like texture
- Acrylic: Lightweight and warm
Characteristics of Natural Fabrics
Natural fabrics like cotton, wool, silk, and linen offer superior comfort and environmental benefits while being gentle on sensitive skin.
Breathability and Comfort
Natural fibers allow air to flow freely through the fabric, helping regulate your body temperature. Cotton and linen are especially good at absorbing moisture from your skin.
Your skin can breathe easier in natural fabrics during hot weather. The fibers adapt to your body’s needs by absorbing sweat when you’re active and releasing it when you cool down.
Natural fabrics move and drape with your body’s movements. They feel soft against your skin and become more comfortable over time with proper care.
Hypoallergenic Properties
Natural fibers minimize skin irritation and allergic reactions. Pure cotton and organic cotton are ideal choices if you have sensitive skin.
The absence of artificial chemicals in natural fabrics reduces the risk of skin rashes and irritation. Your skin is less likely to react negatively to natural materials.
Hemp and linen naturally resist bacteria and microorganisms. This helps prevent odors and makes these fabrics excellent for people with allergies or asthma.
Environmental Benefits
Natural fabrics break down naturally at the end of their life cycle. Cotton, hemp, and jute return to the earth without leaving harmful residues.
Your choice of natural fabrics helps reduce plastic pollution. Unlike synthetic materials, natural fibers don’t release microplastics when washed.
Organic cotton farming uses significantly less water than conventional methods. Hemp grows quickly with minimal water and no pesticides.
Natural fabrics can be recycled or composted. When you choose these materials, you reduce waste in landfills.
Many natural fiber crops support local farming communities. Growing these materials helps maintain biodiversity and soil health.
Characteristics of Synthetic Fabrics
Synthetic fabrics offer unique properties from their chemical processing and artificial origins. These materials combine strength, easy care, and specialized performance features that make them valuable for many uses.
Durability and Use in Fashion
Synthetic fibers provide excellent durability at a lower cost than natural materials. You’ll find these fabrics resist tearing and maintain their shape through repeated wear.
Spandex adds stretch and flexibility to athletic wear and form-fitting clothing. Your workout clothes keep their shape even after many uses thanks to stretchy synthetic fibers.
These materials often cost less while still looking stylish. You can find synthetic versions of expensive natural fabrics like silk and wool at budget-friendly prices.
Moisture-Wicking Abilities
Modern synthetic fabrics excel at moving sweat away from your skin. This makes them ideal for exercise clothes and outdoor gear.
The fibers transport moisture to the outer surface where it can evaporate quickly. Your clothes stay lighter and more comfortable during physical activity.
These materials dry faster than natural fabrics. You won’t feel weighed down by damp clothing during workouts or outdoor adventures.
Water Resistance and Protection
Many synthetic fabrics offer water-resistant properties that natural materials cannot match. DWR (Durable Water Repellent) coatings on synthetic fabrics create excellent protection against light rain and moisture.
Some synthetic materials provide fire resistance, making them essential for protective clothing in industrial settings. These safety features save lives in dangerous work environments.
Maintenance and Use in Various Industries
Synthetic fabrics resist stains better than natural materials. Many have special coatings that make cleaning spills easier.
Care instructions for synthetic fabrics:
- Machine wash in cool or warm water
- Tumble dry on low heat
- Avoid high temperatures that might melt fibers
- No special cleaning products needed
These materials work well in:
- Medical scrubs and protective gear
- Industrial uniforms
- Outdoor equipment
- Home furnishings
The water-resistant nature of synthetic fabrics makes them perfect for raincoats and outdoor gear. Your belongings stay dry even in wet conditions.
Smart Fabrics: The Future of Textiles in 2025
The textile industry is experiencing a revolutionary transformation with smart fabrics leading the charge. These innovative materials combine traditional textile manufacturing with cutting-edge technology to create fabrics that can sense, respond, and interact with their environment.
What Are Smart Fabrics?
Smart fabrics, also called e-textiles, are materials that can change their properties based on environmental conditions or user needs. They can monitor your heart rate, regulate your body temperature, or even charge your electronic devices.
The global smart textiles market is projected to reach $174.11 billion by 2030, growing at an incredible rate of 38.73% annually. This explosive growth shows how quickly this technology is becoming mainstream.
Health Monitoring Capabilities
Modern smart fabrics can track vital signs without bulky devices. Shirts with embedded sensors monitor your heart rate, breathing patterns, and even stress levels throughout the day.
These fabrics are revolutionizing healthcare by allowing continuous patient monitoring. Doctors can track recovery progress and detect health issues before they become serious problems.
Athletic wear with smart fibers helps optimize workout performance. The fabric analyzes your movement patterns and provides real-time feedback to improve your training.
Temperature Regulation Technology
Phase-change materials in smart fabrics automatically adjust to keep you comfortable. When you get warm, the fabric absorbs excess heat. When you cool down, it releases that stored heat back to your body.
This technology is particularly valuable for outdoor workers and athletes who face changing weather conditions throughout the day.
Conductive Fibers and Connectivity
Smart fabrics incorporate conductive threads that can transmit data wirelessly. Your clothing becomes part of your personal network, connecting seamlessly with smartphones and fitness apps.
Some smart fabrics can harvest energy from your movement or body heat, eliminating the need for external batteries. This makes them practical for everyday wear.
Applications Across Industries
Healthcare: Hospital gowns that monitor patient vital signs and alert nurses to changes in condition.
Sports: Athletic wear that tracks performance metrics and prevents injuries through real-time feedback.
Military: Uniforms that provide communication capabilities and monitor soldier health in combat situations.
Fashion: Clothing that changes color or pattern based on mood or environmental factors.
Environmental Impact of Fabric Production
The production of both natural and synthetic fabrics creates distinct challenges for the environment through water usage, chemical processes, and long-term ecological effects. Your fabric choices can make a big difference in reducing environmental harm.
Sustainable Production Practices
Cotton farming requires 2,700 liters of water to produce just one t-shirt. This high water usage puts pressure on local water supplies.
Renewable materials like hemp and bamboo need less water and fewer pesticides to grow. These crops can thrive without depleting soil nutrients.
Ways to spot sustainable production:
- Look for organic certification labels
- Check for recycled content percentages
- Verify water recycling practices
- Seek out renewable energy usage
Chemical Use and Pollution
Synthetic fiber production involves complex chemical processes that can release harmful substances into water and air.
Your synthetic clothes shed microfibers in the wash. These tiny plastic particles end up in oceans and harm marine life.
Natural fabrics aren’t perfect either. Traditional cotton farming uses more pesticides than most other crops.
Common fabric pollutants:
- Dyes and bleaching agents
- Plastic microfibers
- Agricultural chemicals
- Processing solvents
Textile Recycling and Circular Economy
The textile recycling market is forecasted to reach $5.67 billion by 2030, growing at 5.54% annually as consumers demand more sustainable options.
Innovative recycling methods:
- Mechanical recycling: Physically breaks down textiles into fibers for new yarns
- Chemical recycling: Breaks down materials at the molecular level for fiber-to-fiber recycling
- Enzymatic recycling: Uses enzymes to break down natural fibers like cotton
Major brands like Zara are investing in automated systems that reduce material waste while maintaining fast fashion cycles.
Long-Term Sustainability
Recycled polyester (RPET) offers a way to reuse plastic waste while reducing new plastic production.
Your natural fiber clothes will break down at the end of their life. Synthetic fabrics can take hundreds of years to decompose.
Sustainable fabric innovations:
- Biodegradable synthetics
- Closed-loop manufacturing
- Zero-waste cutting
- Fiber recycling technology
Choose fabrics made with renewable resources when possible. Look for companies that use clean energy and minimize chemical waste in their production.
Comparison of Natural and Synthetic Fabric Qualities
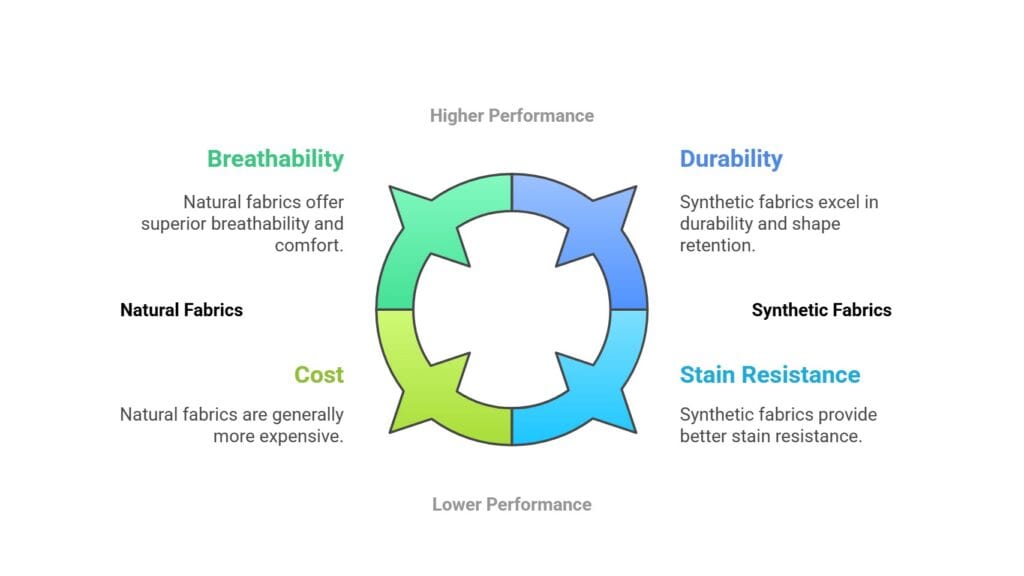
Natural fabrics like cotton, wool, and silk offer excellent breathability and comfort against your skin. These materials let air flow freely and absorb moisture well, making them perfect for everyday wear.
Synthetic materials tend to be more durable and keep their shape better than natural fibers. Your synthetic clothing will resist wrinkles, maintain its structure, and often last longer through repeated washing.
When it comes to cost, synthetic fabrics are typically more affordable. You can find budget-friendly options that look good and perform well for daily use.
Natural fabrics have superior absorbency properties. Your cotton t-shirt will soak up sweat better than a polyester one, though it may take longer to dry.
Performance Comparison Table
| Feature | Natural Fabrics | Synthetic Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability | Excellent | Good to Fair |
| Moisture Absorption | High | Low to Medium |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
| Shape Retention | Fair | Excellent |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Stain Resistance | Fair | Good |
| Wrinkle Resistance | Poor to Fair | Excellent |
| UV Protection | Variable | Often Enhanced |
Key Differences:
- Natural: More breathable, better moisture absorption
- Synthetic: More durable, better shape retention
- Natural: Higher cost, premium feel
- Synthetic: Stain resistant and water-resistant
The structure of synthetic fabrics remains consistent over time. Your synthetic garments will resist stretching and shrinking better than natural materials.
Both fabric types can be comfortable, but natural fibers often feel softer against your skin. Your choice might depend on the specific use – natural fabrics for comfort and breathability, synthetics for durability and easy care.
Fabric Identification Guide
How Can You Tell if Fabric is Natural or Synthetic?
Learning to identify fabric types helps you make better purchasing decisions and care for your clothes properly.
Visual and Touch Tests:
- Natural fabrics often have slight irregularities in texture and may feel softer
- Synthetic fabrics typically have uniform texture and may feel smoother or more slippery
The Burn Test (Use with Caution):
- Natural fibers burn and produce ash, smelling like burning paper or hair
- Cotton and linen burn quickly with a bright flame
- Wool and silk burn slowly and smell like burning hair
- Synthetic fibers melt and create hard plastic-like beads
- Polyester and nylon melt before burning and smell chemical-like
Water Drop Test:
- Natural fabrics like cotton and linen absorb water quickly
- Synthetic fabrics often repel water or absorb it slowly
See visual guide below:
Fabric Identification Guide
Learn to identify natural and synthetic fabrics with these simple, reliable methods
Visual & Touch Test
The easiest way to start identifying fabric type is through visual inspection and feel.
- Slight irregularities in texture
- Softer, more natural feel
- May have visible fiber variations
- Often feels breathable
- Uniform, consistent texture
- Smoother or slippery feel
- Perfect pattern consistency
- May feel less breathable
Water Drop Test
Test how fabric responds to water to determine its absorbency properties.
- Absorb water quickly
- Water spreads into fabric
- Cotton and linen soak up water
- Wool absorbs slowly but steadily
- Often repel water
- Water beads on surface
- Absorb water very slowly
- May have water-resistant treatments
Burn Test
The most definitive test, but requires extreme caution and should only be done by adults.
- Burns and produces ash
- Cotton/linen: burns quickly, bright flame
- Wool/silk: burns slowly, smells like hair
- Creates soft, gray ash
- Melts before burning
- Creates hard, plastic-like beads
- Chemical smell when burning
- May drip molten material
Label Reading
The most reliable method – always check fabric content labels first.
- Fiber content percentages
- Care instruction symbols
- Country of origin
- Brand certifications
- 100% Cotton (natural)
- Polyester blend (synthetic)
- Cotton/Spandex mix (blend)
- Care symbols indicate fabric type
Burn Test Warning: Only perform burn tests in a safe, well-ventilated area with water nearby. Use a small, inconspicuous sample. Never burn synthetic fabrics indoors as they can release toxic fumes. Always supervise children and prioritize safety over testing.
| Fabric | Type | Feel | Water Response | Burn Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Natural | Soft, breathable | Absorbs quickly | Burns fast, smells like paper |
| Linen | Natural | Crisp, textured | Very absorbent | Burns quickly, bright flame |
| Wool | Natural | Soft, warm | Absorbs slowly | Burns slowly, smells like hair |
| Silk | Natural | Smooth, luxurious | Moderate absorption | Burns slowly, hair-like smell |
| Polyester | Synthetic | Smooth, uniform | Water-resistant | Melts, hard beads, chemical smell |
| Nylon | Synthetic | Slippery, strong | Repels water | Melts quickly, chemical odor |
| Rayon | Semi-synthetic | Silk-like, soft | Absorbs well | Burns like cotton but may melt |
| Acrylic | Synthetic | Wool-like, light | Water-resistant | Melts and burns, acrid smell |
Quick Identification Tips
Common Fabric Questions Answered
Is denim natural or synthetic? Traditional denim is made from 100% cotton, making it a natural fabric. However, modern stretch denim often contains 2-5% elastane or spandex for flexibility.
Are towels synthetic or cotton? Most quality towels are made from 100% cotton for maximum absorbency. Some budget towels may contain synthetic blends, but pure cotton performs better for drying.
Is linen natural or synthetic? Linen is a completely natural fabric made from flax plants. It’s one of the oldest textiles in the world and offers excellent breathability for warm weather clothing.
Is silk a natural fiber? Yes, silk is a natural protein fiber produced by silkworms. It’s prized for its smooth texture and natural temperature-regulating properties.
Is wool man-made or natural? Wool is entirely natural, coming from sheep and other animals like alpacas and goats. It provides excellent insulation and moisture-wicking properties.
What is corduroy made of? Corduroy can be made from cotton (natural), polyester (synthetic), or cotton-polyester blends. The fabric is distinguished by its raised ridges called wales.
Is velvet natural or synthetic? Velvet can be either natural or synthetic. Traditional velvet was made from silk, but modern versions often use cotton, polyester, or rayon. Check the label to determine the fiber content.
Can vegans wear velvet? It depends on the fabric content. Silk velvet is not vegan-friendly, but cotton, polyester, or rayon velvet are suitable for vegans.
Is chiffon natural or synthetic? Chiffon can be made from silk (natural), polyester (synthetic), or nylon (synthetic). The manufacturing process creates the lightweight, sheer texture regardless of fiber content.
Is felt natural or synthetic? Felt can be made from wool (natural), synthetic fibers, or blends. Traditional felt uses wool fibers that are matted together through heat and pressure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Natural Fabrics
Advantages of Natural Fabrics
Comfort and Breathability Natural fibers excel at temperature regulation and moisture management. Cotton and linen keep you cool in summer, while wool provides warmth in winter without overheating.
Skin-Friendly Properties Natural fabrics rarely cause allergic reactions or skin irritation. They’re ideal for people with sensitive skin or conditions like eczema.
Environmental Benefits Natural fabrics biodegrade completely at the end of their lifecycle. They don’t contribute to microplastic pollution in oceans.
Absorbency Natural fibers absorb moisture effectively, making them comfortable to wear and excellent for towels and bedding.
Ageing Quality Natural fabrics often improve with age, becoming softer and more comfortable over time.
Disadvantages of Natural Fabrics
Higher Cost Natural fabrics typically cost more than synthetic alternatives due to farming, harvesting, and processing expenses.
Maintenance Requirements Many natural fabrics require special care, including hand washing, air drying, or professional cleaning.
Wrinkle Tendency Natural fabrics like cotton and linen wrinkle easily and may need frequent ironing.
Shrinkage Risk Natural fibers can shrink when exposed to heat or improper washing, potentially ruining garments.
Color Fading Natural dyes and fibers may fade more quickly than synthetic alternatives when exposed to sunlight and washing.
Seasonal Limitations Some natural fabrics perform poorly in specific conditions. Cotton becomes heavy when wet, and wool can be too warm for summer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Synthetic Fabrics
Advantages of Synthetic Fabrics
Durability and Longevity Synthetic fabrics resist wear and tear better than natural materials. They maintain their shape and color through numerous wash cycles.
Easy Care Most synthetic fabrics are machine washable and dry quickly. They rarely need ironing or special treatment.
Cost-Effectiveness Synthetic materials offer good performance at lower prices, making quality clothing accessible to more people.
Specialized Performance Synthetic fabrics can be engineered for specific purposes like moisture-wicking, water resistance, or UV protection.
Consistency Synthetic manufacturing produces uniform quality and properties, ensuring predictable performance.
Versatility Synthetic fibers can mimic the appearance and feel of expensive natural fabrics at a fraction of the cost.
Disadvantages of Synthetic Fabrics
Limited Breathability Synthetic fabrics often trap heat and moisture, making them uncomfortable in warm weather or during physical activity.
Environmental Concerns Synthetic fabric production relies on petroleum products and releases microplastics into waterways during washing.
Static Buildup Synthetic materials tend to generate static electricity, causing clothes to cling and attract lint.
Odor Retention Some synthetic fabrics trap odors more readily than natural materials, requiring more frequent washing.
Heat Sensitivity High temperatures can damage synthetic fabrics, causing melting or permanent deformation.
Potential Skin Reactions Some people experience skin irritation from certain synthetic materials, especially during extended wear.
See the visual comparison below:
Natural vs Synthetic Fabrics
Complete comparison of advantages and disadvantages to help you make informed choices
Natural Fabrics
Cotton, Wool, Silk, Linen & More
- Superior Breathability: Allow air circulation for temperature regulation
- Comfort & Softness: Feel natural and gentle against skin
- Hypoallergenic: Rarely cause skin irritation or allergic reactions
- Moisture Absorption: Excellent at wicking away sweat and moisture
- Biodegradable: Decompose naturally without environmental harm
- Temperature Adaptive: Adjust to body temperature changes
- Improve with Age: Often become softer and more comfortable over time
- No Microplastics: Don’t shed harmful particles when washed
- Higher Cost: Generally 20-50% more expensive than synthetics
- Wrinkle Easily: Require more maintenance and ironing
- Shrinkage Risk: Can shrink when exposed to heat or improper washing
- Special Care: Often need gentle washing, air drying, or dry cleaning
- Color Fading: Natural dyes may fade faster than synthetic colors
- Slower Drying: Take longer to dry than synthetic alternatives
- Seasonal Limitations: Some perform poorly in specific weather conditions
- Inconsistent Quality: Natural variations can affect uniformity
Synthetic Fabrics
Polyester, Nylon, Acrylic & More
- Excellent Durability: Resist tearing and maintain shape through repeated use
- Easy Care: Machine washable with simple maintenance requirements
- Cost-Effective: More affordable while maintaining good performance
- Wrinkle Resistant: Maintain smooth appearance without ironing
- Quick Drying: Dry faster than natural fabrics
- Stain Resistant: Repel spills and clean easily
- Consistent Quality: Uniform manufacturing ensures predictable results
- Specialized Features: Can be engineered for specific performance needs
- Limited Breathability: Trap heat and moisture, causing discomfort
- Environmental Impact: Made from petroleum products, shed microplastics
- Static Buildup: Generate static electricity, attract lint
- Odor Retention: Trap odors more readily than natural materials
- Heat Sensitivity: Can melt or deform when exposed to high temperatures
- Potential Skin Reactions: May cause irritation in sensitive individuals
- Long Decomposition: Take 200-500 years to break down in landfills
- Less Comfortable: May feel artificial or uncomfortable for extended wear
Quick Performance Comparison
| Feature | Natural Fabrics | Synthetic Fabrics |
|---|---|---|
| Breathability | Excellent | Fair |
| Durability | Good | Excellent |
| Easy Care | Fair | Excellent |
| Comfort | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | Excellent | Poor |
| Moisture Management | Excellent | Good |
| Shape Retention | Fair | Excellent |
Making the Right Choice
Health and Safety Considerations
Does Polyester Get Absorbed Through Skin?
Polyester fibers themselves don’t penetrate the skin barrier. However, some people worry about chemical treatments used in synthetic fabric processing.
The skin acts as an effective barrier against fabric fibers. Any skin reactions typically result from surface irritation rather than absorption.
Why Should We Avoid Using Synthetic Materials?
While synthetic fabrics have many benefits, some concerns include:
Environmental Impact: Microplastic pollution and petroleum dependency Comfort Issues: Reduced breathability and potential for odor retention Static Problems: Synthetic materials can generate uncomfortable static electricity
However, complete avoidance isn’t necessary. Choose synthetic fabrics wisely for appropriate applications while preferring natural materials for everyday comfort.
Synthetic Fiber Decomposition
Synthetic fibers can take 200-500 years to decompose completely in landfills. This long decomposition time contributes to textile waste problems globally.
Recent innovations in biodegradable synthetics aim to address this issue while maintaining the performance benefits of traditional synthetic materials.
Innovations in Fabric Technologies
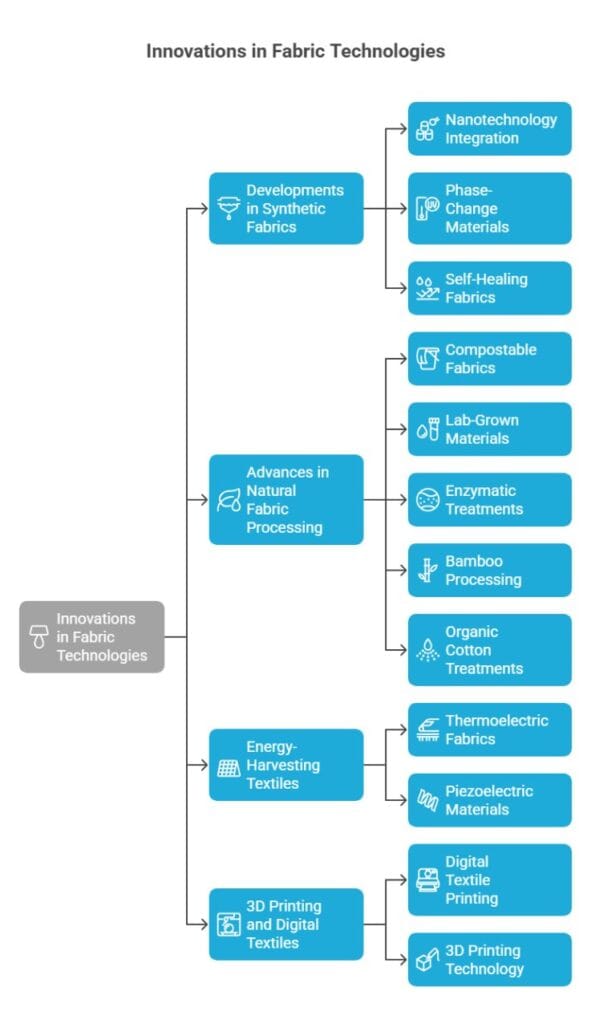
Recent breakthroughs in textile engineering have created fabrics that combine comfort with cutting-edge functionality. Smart textiles can now monitor health metrics while maintaining comfort and durability.
Developments in Synthetic Fabrics
Modern synthetic fibers offer enhanced performance through specialized chemical processes. You’ll find these innovations in moisture-wicking athletic wear and wrinkle-resistant business attire.
Nanotechnology Integration: Manufacturers are incorporating silver and gold nanoparticles into synthetic fabrics to provide antimicrobial properties and enhanced durability.
Phase-Change Materials: These advanced synthetics can store and release thermal energy, helping regulate body temperature automatically.
Self-Healing Fabrics: New synthetic materials can repair small tears and holes automatically, extending garment lifespan significantly.
Semi-synthetic fabrics like Modal and Lyocell bridge the gap between natural and synthetic materials. These fabrics start with wood pulp and transform through eco-friendly processes.
Blended fabrics combine the best qualities of multiple fiber types. A polyester-cotton blend gives you durability with breathability.
Advances in Natural Fabric Processing
Compostable fabrics made from biodegradable materials break down naturally after use. This reduces textile waste in landfills.
Lab-Grown Materials: Scientists are developing bio-fabricated materials like lab-grown cotton and mushroom-based leather alternatives that offer sustainable options without traditional farming.
Enzymatic Treatments: New enzyme-based processing methods enhance natural fabric properties without harsh chemicals, improving durability and performance.
Bamboo processing has evolved to create softer, more durable textiles. The fast-growing plant produces fabric that’s naturally antimicrobial and moisture-wicking.
New organic cotton treatments enhance its natural properties without harmful chemicals. These treatments improve water resistance and durability while maintaining cotton’s breathability.
Energy-Harvesting Textiles
Revolutionary fabrics can now generate electricity from body movement, temperature differences, or solar energy. These textiles can power small electronic devices embedded in clothing.
Thermoelectric fabrics convert body heat into electrical energy, while piezoelectric materials generate power from mechanical stress and movement.
3D Printing and Digital Textiles
Digital textile printing allows for complex patterns and designs impossible with traditional methods. 3D printing technology creates entirely new textile structures with customized properties.
These technologies enable on-demand production, reducing waste and allowing for personalized fit and design.
The Role of Fabrics in the Fashion Industry

When you shop for clothes, you’re part of a massive global textile network. The fashion and textile industries rely on both natural and synthetic materials to create the clothes you wear every day.
Your clothing choices impact the environment in different ways. Natural fabrics offer comfort and sustainability, while synthetic materials provide durability at a lower cost.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
The manufacturing process varies greatly between fabric types:
- Natural Fabrics: Need farming, harvesting, and processing
- Synthetic Fabrics: Require chemical processing and oil-based materials
- Blended Fabrics: Combine both natural and synthetic fibers
Your clothes face daily wear and tear, which affects how long they last. Synthetic materials often show better durability in tough conditions, making them popular for sportswear and outdoor clothing.
Sustainability in Fashion
Sustainable production is becoming more important in fashion. You can now find:
- Recycled polyester clothing
- Organic cotton items
- Low-impact dyed fabrics
- Water-conserving production methods
The fashion industry uses different fabrics based on:
- Price points
- Target market
- Season
- Intended use
- Environmental impact
Fast Fashion vs. Sustainable Fashion
Fast fashion relies heavily on synthetic materials for quick, affordable production. However, this approach contributes to environmental problems and poor working conditions.
Sustainable fashion emphasizes quality over quantity, often using natural or recycled materials. This approach costs more upfront but provides better long-term value.
Regional Production Trends
Asia-Pacific: Dominates manufacturing with cost-effective production and established supply chains Europe: Focuses on high-quality, sustainable production and innovative technologies North America: Emphasizes smart textiles and technical performance fabrics
Fabric Selection Guide by Use Case

Athletic and Performance Wear
Best Choices: Moisture-wicking synthetics like polyester blends, nylon, and spandex combinations
Modern athletic wear requires fabrics that move moisture away from skin while providing flexibility and durability. Lightweight synthetic fabrics excel in these applications.
Key Features:
- Quick-drying properties
- Four-way stretch capability
- Antimicrobial treatments
- UV protection
Professional and Business Attire
Best Choices: Wool blends, cotton-polyester combinations, and high-quality synthetics
Professional clothing needs to look polished while maintaining comfort throughout long work days. Wrinkle-resistant synthetic blends reduce maintenance while natural fibers provide breathability.
Key Features:
- Wrinkle resistance
- Shape retention
- Professional appearance
- Easy care requirements
Casual and Everyday Wear
Best Choices: Cotton, cotton blends, and comfortable synthetic alternatives
Daily wear prioritizes comfort and ease of care. Natural cotton provides breathability, while synthetic blends add durability and reduce shrinkage.
Outdoor and Adventure Gear
Best Choices: Technical synthetics with specialized coatings
Outdoor clothing must protect against weather while allowing freedom of movement. Water-resistant and waterproof fabrics keep you dry, while insulating materials maintain warmth.
Essential Features:
- Weather protection
- Durability
- Packability
- Temperature regulation
Children’s Clothing
Best Choices: Soft natural fibers and gentle synthetic blends
Children’s sensitive skin requires gentle fabrics that resist stains and frequent washing. Organic cotton and bamboo provide comfort, while synthetic blends add durability for active play.
Important Considerations:
- Hypoallergenic properties
- Easy washing
- Stain resistance
- Safety (flame resistance for sleepwear)
See visual use case guide below:
Fabric Selection Guide by Use Case
Choose the perfect fabric for every situation with our comprehensive selection guide
Quick Fabric Selector
Athletic & Performance Wear
- Polyester Blends
- Nylon
- Spandex Mix
- Merino Wool
- Bamboo Blends
- Technical Synthetics
Prioritize performance over appearance. Look for fabrics that move moisture away from skin while providing flexibility and durability for high-intensity activities.
Professional & Business Attire
- Wool Blends
- Cotton-Polyester
- High-Quality Synthetics
- Linen Blends
- Modal
- Tencel
Balance professional appearance with comfort for long work days. Choose fabrics that maintain their shape and resist wrinkles while allowing breathability.
Casual & Everyday Wear
- 100% Cotton
- Cotton Blends
- Soft Synthetics
- Jersey Knits
- French Terry
- Bamboo
Prioritize comfort and ease of care. Natural fibers provide breathability, while blends add durability and reduce shrinkage for everyday practicality.
Outdoor & Adventure Gear
- Technical Synthetics
- DWR-Coated Fabrics
- Ripstop Nylon
- Softshell Materials
- Insulated Synthetics
- Merino Wool
Focus on protection against elements while maintaining mobility. Layer-friendly fabrics with specialized coatings provide versatility for changing conditions.
Children’s Clothing
- Organic Cotton
- Bamboo
- Soft Synthetic Blends
- Modal
- Cotton Jersey
- Flame-Resistant (Sleepwear)
Sensitive skin requires gentle fabrics that resist stains and frequent washing. Safety features like flame resistance are essential for sleepwear.
Special Occasions
- Silk
- Fine Wool
- Luxe Synthetics
- Satin
- Chiffon
- Velvet
Appearance and elegance take priority over practicality. Choose fabrics that photograph well and create the desired formal impression.
Fabric Priority Matrix by Use Case
| Use Case | Comfort | Durability | Appearance | Performance | Easy Care | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athletic Wear | High | High | Low | High | Medium | Medium |
| Professional | Medium | Medium | High | Low | High | Medium |
| Casual Daily | High | Medium | Medium | Low | High | High |
| Outdoor Gear | Medium | High | Low | High | Medium | Low |
| Children’s | High | High | Medium | Low | High | Medium |
| Special Occasions | Medium | Low | High | Low | Low | Low |
Cost Analysis and Value Comparison

Initial Purchase Price
Natural fabrics typically cost 20-50% more than synthetic alternatives due to:
- Agricultural production costs
- Processing complexity
- Limited growing seasons
- Labor-intensive harvesting
Synthetic fabrics offer lower upfront costs through:
- Efficient mass production
- Consistent year-round manufacturing
- Automated processing
- Economies of scale
Long-Term Value Assessment
Natural Fabrics:
- Higher initial cost but often longer-lasting quality
- May require more expensive care (dry cleaning, special detergents)
- Can improve with age when properly maintained
- Higher resale value for quality pieces
Synthetic Fabrics:
- Lower purchase price but may need replacement sooner
- Minimal care costs (machine washable)
- Consistent performance over time
- Limited resale value
Cost Per Wear Analysis
Calculate true value by dividing total cost (purchase + care) by number of wears:
Example: A $60 cotton shirt worn 100 times costs $0.60 per wear, while a $30 polyester shirt worn 50 times costs $0.60 per wear, making the values equivalent.
Hidden Environmental Costs
Consider environmental impact in cost calculations:
- Natural fabrics may have lower long-term environmental costs
- Synthetic fabrics contribute to microplastic pollution cleanup costs
- Recycling and disposal expenses vary significantly between fabric types
Real-time interactive cost-per-wear calculator with live updates:
Cost Analysis and Value Comparison
Understanding the true cost of fabric choices to make informed purchasing decisions
Natural Fabrics
Higher upfront, better long-term value
- Agricultural Production High
- Processing Complexity High
- Labor Intensive High
- Seasonal Limitations Medium
- Quality Variations Medium
Synthetic Fabrics
Lower upfront, variable long-term cost
- Mass Production Low
- Automated Processing Low
- Consistent Manufacturing Low
- Year-round Production Low
- Economies of Scale High
Cost Per Wear Calculator
Calculate the true value of your fabric investment
| Fabric Type | Initial Cost | Care Costs (5yr) | Replacement Rate | Total 5-Year Cost | Cost per Wear |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Premium Cotton | $50 | $20 | 0.5x | $95 | $0.63 |
| Polyester Blend | $25 | $8 | 1.5x | $71 | $0.59 |
| Linen | $75 | $25 | 0.3x | $123 | $0.77 |
| Wool | $90 | $45 | 0.5x | $180 | $0.90 |
| Athletic Synthetic | $40 | $10 | 1.2x | $88 | $0.66 |
| Budget Cotton | $20 | $12 | 2x | $84 | $0.84 |
Return on Investment Analysis
Value Optimization Strategies
Hidden Environmental Costs
Care and Maintenance Guidelines
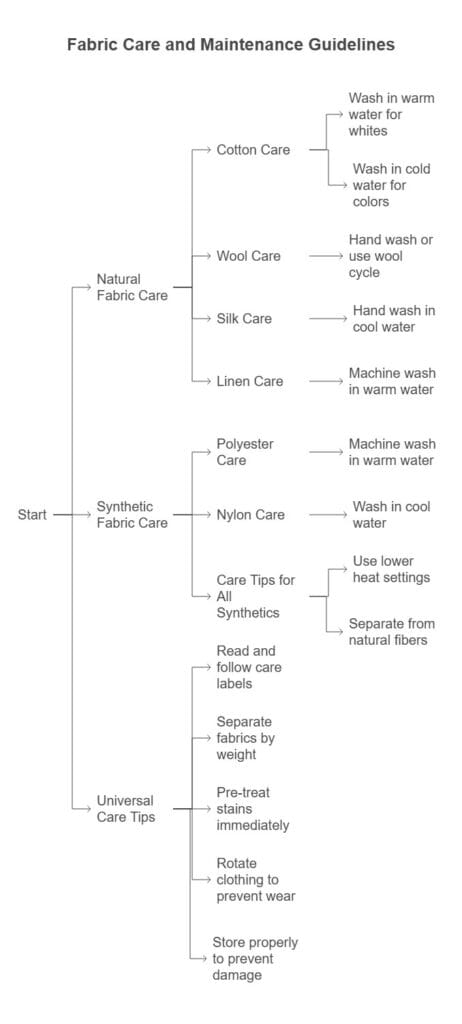
Natural Fabric Care
Cotton Care:
- Wash in warm water for whites, cold for colors
- Use gentle detergents without bleach
- Air dry when possible to prevent shrinkage
- Iron while slightly damp for best results
Wool Care:
- Hand wash or use wool cycle with cold water
- Use wool-specific detergents
- Never wring or twist wet wool
- Lay flat to dry away from direct heat
Silk Care:
- Hand wash in cool water with gentle detergent
- Never use bleach or fabric softener
- Press while damp using low heat
- Store on padded hangers
Linen Care:
- Machine wash in warm water
- Expects some wrinkles (part of linen’s character)
- Iron while damp for smoothest results
- Improves with each washing
Synthetic Fabric Care
Polyester Care:
- Machine wash in warm water
- Use regular detergent
- Tumble dry on low heat
- Remove promptly to prevent wrinkles
Nylon Care:
- Wash in cool water to prevent shrinkage
- Avoid fabric softeners (reduces moisture-wicking)
- Air dry when possible
- Store away from sharp objects
Care Tips for All Synthetics:
- Use lower heat settings
- Separate from natural fibers to prevent pilling
- Remove stains quickly before they set
- Check care labels for specific requirements
Universal Care Tips
- Read and follow care labels religiously
- Separate fabrics by weight and care requirements
- Pre-treat stains immediately
- Rotate clothing to prevent excessive wear
- Store properly to maintain shape and prevent damage
Market Trends and Future Predictions
Current Market Data
The global textile market reached $2.12 trillion in 2025 and projects growth to $4.01 trillion by 2034, representing a 7.35% compound annual growth rate.
Key growth drivers include:
- Increasing demand for sustainable materials
- Smart textile technology advancement
- Rising disposable income in developing markets
- E-commerce expansion
Emerging Technologies
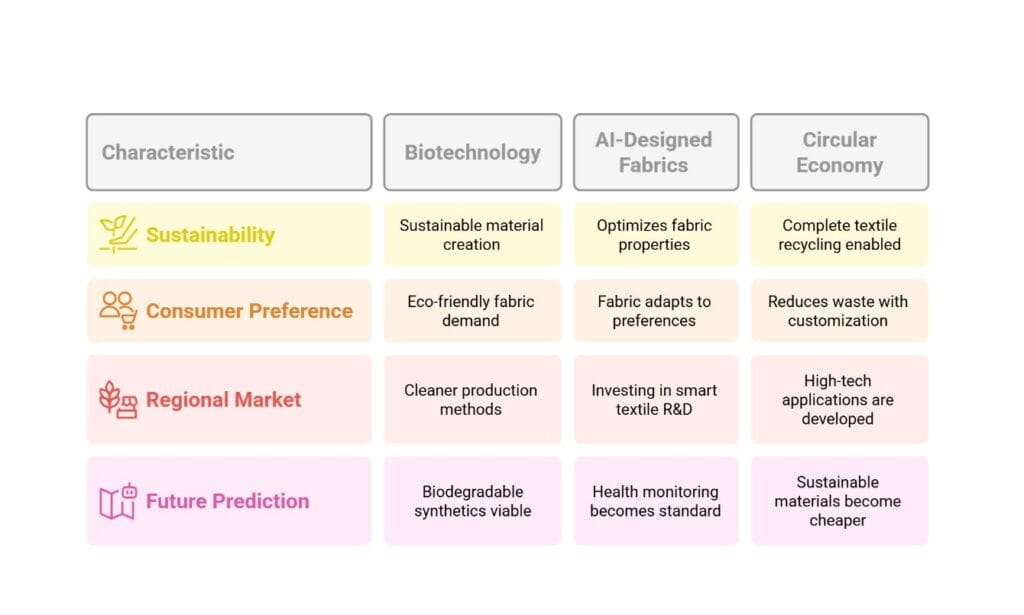
Biotechnology Integration: Scientists are developing fabrics from algae, bacterial cellulose, and other microorganisms, creating entirely new categories of sustainable materials.
AI-Designed Fabrics: Artificial intelligence helps optimize fabric properties by predicting performance characteristics and consumer preferences.
Circular Economy Solutions: New technologies enable complete textile recycling, turning old clothes into new fibers without quality loss.
Consumer Preference Shifts
Sustainability Focus: 73% of consumers willing to pay more for sustainable products, driving demand for eco-friendly fabrics.
Performance Requirements: Increasing demand for multi-functional fabrics that combine comfort, durability, and specialized features.
Personalization: Growing interest in customized fabrics that adapt to individual needs and preferences.
Regional Market Developments
Asia-Pacific: Continues manufacturing dominance while investing heavily in smart textile research and development.
Europe: Leading sustainable innovation with strict environmental regulations driving cleaner production methods.
North America: Focusing on high-tech applications and military/medical textile development.
Future Predictions (2025-2030)
Technology Integration: Expect widespread adoption of smart textiles in everyday clothing, with basic health monitoring becoming standard.
Sustainability Breakthroughs: Biodegradable synthetics and lab-grown materials will become commercially viable alternatives.
Personalized Production: On-demand manufacturing will reduce waste while providing customized fit and performance characteristics.
Price Convergence: Sustainable materials will approach cost parity with traditional options through improved production efficiency.
Interactive Fabric Selection Tool
Interactive Fabric Selection Tool
Answer a few questions to find the perfect fabric for your needs
Quick Recommendations
What’s your primary need?
Your Recommended Fabrics
Based on your preferences, here are the best fabric choices
Quick Decision Flowchart
Fabric Comparison Calculator
Environmental Impact Comparison
| Fabric Type | Water Usage (per t-shirt) | CO2 Emissions | Decomposition Time | Microplastic Release |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Cotton | 1,800 liters | Low | 2-5 months | None |
| Conventional Cotton | 2,700 liters | Medium | 2-5 months | None |
| Polyester | 70 liters | High | 200-500 years | High |
| Recycled Polyester | 45 liters | Medium | 200-500 years | Medium |
| Linen | 500 liters | Very Low | 2-3 weeks | None |
| Hemp | 300 liters | Very Low | 2-3 weeks | None |
| Wool | 4,400 liters | Medium | 1-12 months | None |
| Bamboo | 250 liters | Low | 4-6 months | None |
Cost Analysis Over 5 Years
| Fabric Type | Initial Cost | Care Costs | Replacement Rate | Total 5-Year Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Cotton | $40 | $15 | 1 replacement | $95 |
| Polyester Blend | $25 | $5 | 2 replacements | $80 |
| Linen | $60 | $20 | 0.5 replacements | $110 |
| Wool | $80 | $40 | 0.5 replacements | $160 |
| Synthetic Athletic | $35 | $8 | 1.5 replacements | $95 |
Costs are estimates based on average quality garments and typical use patterns.
Care Instructions Quick Reference
Natural Fabric Care Chart
| Fabric | Water Temp | Drying Method | Ironing | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | Warm/Cold | Air or low heat | Medium heat | Pre-treat stains |
| Linen | Warm | Air dry preferred | High heat while damp | Expects wrinkles |
| Wool | Cold | Lay flat | Low heat with steam | Use wool detergent |
| Silk | Cold | Air dry in shade | Low heat, inside out | No bleach ever |
| Hemp | Warm | Air or low heat | Medium heat | Softens with use |
| Bamboo | Cold/Warm | Air or low heat | Low heat | Very gentle cycle |
Synthetic Fabric Care Chart
| Fabric | Water Temp | Drying Method | Ironing | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester | Warm | Low heat tumble | Low heat | Remove promptly |
| Nylon | Cool | Air dry preferred | Very low heat | Snag easily |
| Acrylic | Cool | Low heat tumble | Low heat through cloth | Static prone |
| Spandex/Elastane | Cool | Air dry | No direct heat | Chlorine damages |
| Rayon | Cool | Air dry | Medium heat while damp | Shrinks easily |
| Modal | Cool/Warm | Low heat tumble | Low heat | Color-fast |
Sustainability Certifications Guide
Key Certifications to Look For
GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard)
- Ensures organic fiber content
- Verifies environmental and social standards
- Covers entire supply chain
OEKO-TEX Standard 100
- Tests for harmful substances
- Ensures human-ecological safety
- Covers all production stages
Cradle to Cradle Certified
- Assesses entire product lifecycle
- Evaluates material health and renewable energy use
- Promotes circular economy principles
bluesign approved
- Focuses on chemical management
- Ensures worker and consumer safety
- Promotes resource efficiency
Better Cotton Initiative (BCI)
- Promotes sustainable cotton farming
- Reduces environmental impact
- Improves farmer livelihoods
How to Verify Certifications
- Check garment labels for certification logos
- Visit certification websites to verify claims
- Research brand sustainability commitments
- Look for transparent supply chain information
Regional Fabric Preferences and Climate Considerations
Climate-Based Fabric Selection
Hot, Humid Climates
- Prioritize breathable natural fibers
- Choose light colors and loose weaves
- Avoid heavy synthetics that trap moisture
- Best options: Cotton, linen, bamboo
Hot, Dry Climates
- Select fabrics that provide UV protection
- Choose materials that don’t retain odors
- Consider moisture-wicking properties
- Best options: Cotton blends, UV-protective synthetics
Cold Climates
- Focus on insulating properties
- Layer different fabric types
- Choose wind-resistant outer layers
- Best options: Wool, fleece, insulated synthetics
Variable/Temperate Climates
- Select versatile, layerable fabrics
- Choose wrinkle-resistant options for travel
- Consider transition-friendly materials
- Best options: Cotton blends, versatile synthetics
Cultural and Regional Preferences
North America: High demand for performance fabrics and easy-care synthetics Europe: Strong preference for sustainable and organic materials Asia: Growing interest in smart textiles and technological integration Middle East: Focus on breathable, modest coverage fabrics Tropical Regions: Emphasis on lightweight, quick-dry materials
Smart Shopping Strategies
Reading Fabric Labels Effectively
Fiber Content: Listed by percentage, highest first Care Instructions: Follow symbols and written instructions Country of Origin: Indicates manufacturing location Certifications: Look for sustainability and safety logos
Questions to Ask When Shopping
- What percentage of each fiber is included?
- How was the fabric treated or finished?
- What certifications does the product have?
- What’s the expected lifespan of this garment?
- How should I care for this fabric?
Red Flags to Avoid
- Missing or unclear care instructions
- Unusually low prices for claimed quality
- Strong chemical odors
- Poor construction quality
- No information about fiber content
Building a Versatile Wardrobe
Foundation Pieces (Natural Fabrics):
- White cotton button-down shirt
- Quality denim jeans
- Wool sweater or cardigan
- Cotton t-shirts in neutral colors
Performance Pieces (Synthetic Fabrics):
- Moisture-wicking athletic wear
- Weather-resistant outer layers
- Quick-dry travel clothing
- Stretchy, comfortable basics
Investment Pieces (High-Quality Blends):
- Professional blazer or jacket
- Versatile dress or trousers
- Quality outerwear
- Specialty items for hobbies/activities
Future Innovations and What to Expect
Emerging Technologies (2025-2030)
Bio-Fabricated Materials
- Lab-grown cotton and silk
- Mushroom-based leather alternatives
- Algae-derived fibers
- Bacterial cellulose textiles
Advanced Smart Textiles
- Health monitoring integration
- Climate-responsive materials
- Self-cleaning fabrics
- Energy-harvesting capabilities
Sustainable Innovations
- Closed-loop recycling systems
- Waterless dyeing technologies
- Carbon-negative production methods
- Biodegradable synthetic alternatives
Market Predictions
Price Trends: Sustainable materials will approach cost parity with conventional options by 2028
Technology Integration: Basic smart textile features will become standard in athletic and outdoor wear
Consumer Behavior: Increased willingness to pay premiums for verified sustainable and ethical production
Regulation: Stricter environmental standards will drive innovation in cleaner production methods
Preparing for Change
As a Consumer:
- Learn about new sustainable options
- Invest in quality pieces that last longer
- Support brands with transparent practices
- Stay informed about care and maintenance
Industry Trends to Watch:
- Blockchain supply chain tracking
- AI-optimized production processes
- Personalized fit technologies
- Rental and sharing economy growth
Conclusion
The choice between natural and synthetic fabrics isn’t simply a matter of one being better than the other. Each category offers distinct advantages that make them suitable for different applications, lifestyles, and values. Natural fabrics excel in comfort, breathability, and environmental friendliness, making them ideal for everyday wear and those with sensitive skin. Synthetic fabrics provide unmatched durability, specialized performance features, and cost-effectiveness, making them essential for athletic wear, outdoor gear, and budget-conscious consumers.
The textile industry in 2025 is experiencing unprecedented innovation. Smart fabrics that monitor health, regulate temperature, and harvest energy represent the future of clothing technology. Meanwhile, sustainable production methods and biodegradable alternatives address growing environmental concerns. The projected growth from $2.12 trillion to $4.01 trillion by 2034 reflects not just increased consumption, but a fundamental shift toward more functional, sustainable, and intelligent textiles.
Your fabric choices carry more weight than ever before. They impact your comfort, health, budget, and environmental footprint. The emergence of smart textiles means clothing will soon become an extension of our digital lives, monitoring our health and adapting to our needs in real-time. Simultaneously, innovations in sustainable production and biodegradable synthetics promise to solve many current environmental challenges.
Key Recommendations
For Everyday Comfort: Choose natural fibers like cotton, linen, and bamboo for clothing that directly contacts your skin. These materials provide superior breathability and comfort for daily wear.
For Performance Activities: Invest in high-quality synthetic fabrics designed for your specific needs. Moisture-wicking polyester blends for exercise, water-resistant synthetics for outdoor adventures, and technical fabrics for professional requirements.
For Environmental Impact: Prioritize organic and sustainably produced natural fibers when possible. Choose recycled synthetic materials and support brands with transparent, sustainable practices. Consider the entire lifecycle cost, including care requirements and longevity.
For Budget Optimization: Calculate cost per wear rather than initial price. Quality natural fabrics and well-made synthetic blends often provide better long-term value despite higher upfront costs.
For Future-Proofing: Stay informed about emerging technologies like smart textiles and sustainable innovations. Consider how new materials might enhance your lifestyle while reducing environmental impact.
The future of textiles lies not in choosing sides between natural and synthetic, but in understanding how each serves specific purposes in our increasingly complex world. Smart shopping means matching fabric properties to your needs while considering long-term environmental and economic impacts. As technology continues advancing, the line between natural and synthetic may blur entirely, giving way to innovative materials that combine the best of both worlds with capabilities we can barely imagine today.
Whether you’re building a sustainable wardrobe, optimizing athletic performance, or simply seeking comfortable daily wear, understanding fabric properties empowers you to make choices that align with your values and needs. The textile revolution is just beginning, and informed consumers will benefit most from the exciting innovations ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are natural fabrics better than synthetic?
Neither natural nor synthetic fabrics are universally “better” – it depends on your specific needs. Natural fabrics excel in breathability, comfort, and environmental friendliness, while synthetics offer superior durability, easy care, and specialized performance features.
The best choice varies by application: cotton for everyday comfort, polyester for athletic wear, wool for warmth, and technical synthetics for outdoor gear.
What are the main problems with synthetic fibers?
The primary concerns with synthetic fibers include limited breathability leading to discomfort, environmental impact from microplastic pollution, dependency on petroleum resources, potential for static buildup, and longer decomposition times (200-500 years). However, many of these issues are being addressed through new technologies and improved manufacturing processes.
How long does it take for synthetic fibers to decompose?
Most synthetic fibers take 200-500 years to decompose completely in landfills. Polyester can take up to 500 years, while nylon takes approximately 200-300 years. This long decomposition time contributes significantly to textile waste problems. However, new biodegradable synthetic alternatives are being developed to address this environmental concern.
Why should we not wear synthetic clothes?
While synthetic clothes have benefits, some people prefer to limit their use due to reduced breathability, potential skin irritation, environmental concerns about microplastic pollution, and static electricity buildup. However, completely avoiding synthetics isn’t necessary or practical. Instead, choose high-quality synthetic fabrics for appropriate applications like athletic wear while preferring natural materials for everyday comfort.
Are Levi jeans 100% cotton?
Traditional Levi’s jeans are made from 100% cotton denim. However, many modern Levi’s styles include small amounts of elastane or spandex (typically 1-3%) for stretch and comfort. Check the label on specific styles, as the company offers both 100% cotton options and stretch varieties to meet different preferences.
Is polyester absorbed through the skin?
No, polyester fibers cannot be absorbed through the skin. The skin acts as an effective barrier against fabric fibers. Any skin reactions from polyester typically result from surface irritation due to reduced breathability or chemical treatments, not from absorption of the material itself.
How can I tell if my fabric is high quality?
High-quality fabrics typically feature consistent weave patterns, smooth texture without pilling, vibrant colors that don’t fade easily, and appropriate weight for their intended use.
Natural fabrics should feel soft and breathable, while quality synthetics should have smooth surfaces and good shape retention. Check the fiber content label and look for reputable brand names or quality certifications.
What’s the difference between organic and conventional cotton?
Organic cotton is grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers, using natural farming methods that protect soil health and water quality. Conventional cotton uses chemical treatments that can be harmful to the environment and farm workers. Organic cotton typically costs more but offers better environmental sustainability and may be gentler on sensitive skin.
Can synthetic fabrics be recycled?
Yes, many synthetic fabrics can be recycled, though the process is more complex than natural fiber recycling. Polyester can be mechanically recycled into new fibers, and some companies use chemical recycling to break down synthetic materials at the molecular level. However, recycling facilities for textiles aren’t widely available, making fabric recycling challenging for consumers.
Which fabrics are best for sensitive skin?
The softest fabrics for sensitive skin include organic cotton, bamboo, silk, and high-quality modal. These materials are naturally hypoallergenic and less likely to cause irritation. Avoid rough textures, synthetic blends with harsh chemicals, and fabrics treated with formaldehyde or other finishing chemicals.
What makes a fabric “breathable”?
Breathable fabrics allow air to flow through the material, helping regulate body temperature and moisture. Natural fibers like cotton and linen have spaces between fibers that permit airflow. Some synthetic fabrics achieve breathability through special weaves or treatments that create air channels. Breathable fabrics are essential for summer clothing and active wear.
How do I choose the right fabric for different seasons?
Spring/Summer: Choose lightweight, breathable fabrics like cotton, linen, and moisture-wicking synthetics. Light colors reflect heat and keep you cooler.
Fall/Winter: Select warm fabrics like wool, fleece, and insulating synthetic materials. Layering different fabric types provides versatile temperature control.
Year-round: Cotton blends and quality synthetic blends work well for transitional weather and indoor environments.




